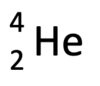Combined Physics - P4 Atomic Structure Flashcards
(40 cards)
Approximately how big is the radius of an atom?
Very small – a radius of about 1x10-10 m
How much smaller is the radius of a nucleus compared with the radius of an atom?
The radius of the nucleus is approximately 1/10,000th the radius of an atom
What happens when electrons fall to a lower energy level (closer to the nucleus)?
They release electromagnetic radiation
What does contamination mean in terms of radioactivity?
If a substance is contaminated, it’s covered in radioactive material.
What two subatomic particles are in the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and Neutrons
What happens if the electrons in an atom absorb electromagnetic radiation?
They move to a higher energy level (further from the nucleus).
What is the overall electrical charge of an atom?
No overall charge – electron and proton numbers are equal
What does irradiation mean?
Exposing an object to nuclear radiation (the object itself does not become radioactive)
What is the mass number of an atom?
The number of protons and neutrons in an atom
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
Before the discovery of the electron, what were atoms thought to be (as suggested by Dalton)?
Tiny spheres that could not be divided
What did Rutherford’s scattering experiment reveal about the atom?
- The mass of the atom was concentrated in the centre (nucleus).
- The nucleus was small.
- The nucleus was positively charged.
What precautions should be taken around hazardous radioactive materials?
- Wearing gloves / using tongs
- Protective suits
- Breathing apparatus
- Limiting exposure time
What happens to an atom if it loses one or more outer electron(s)?
It becomes a positive ion.
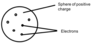
What was the Plum Pudding model?
The atom was suggested to be a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it.
How did Bohr adapt the nuclear model of the atom?
Bohr suggested electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances (energy levels).
List alpha, beta and gamma radiation from most to least ionising.
Alpha (most ionising)
Beta (moderately ionising)
Gamma (least ionising)
Name the three types of radiation that can be emitted by unstable nuclei.
- Alpha radiation
- Beta radiation
- Gamma radiation
What is nuclear ‘activity’ measured in?
Becquerels (Bq) where 1 Bq is 1 decay per second
List alpha, beta and gamma radiation in terms of their range in air (from shortest to longest).
Alpha (shortest range in air, few cm)
Beta (moderate range in air, few m)
Gamma (longest range in air)
What sub-atomic particle was discovered by James Chadwick?
Neutron
List alpha, beta and gamma radiation from most penetrating to least penetrating.
Gamma (most penetrating)
Beta (moderately penetrating)
Alpha (least penetrating)
Name the equipment used to measure radioactivity.
Geiger-Muller Tube
What is alpha (α) radiation?
A helium nucleus (2 neutrons and 2 protons)