Clinical features and Management of Restrictive Lung Diseases Flashcards
(25 cards)
What is the physiological definition of restriction?
Forced vital capacity of less than 80% of predicted normal
Describe the differences between the pulmonary function tests between normal, obstructive and restrictive lung
Obstructive
- Larger TLC, RV, FRC
- Smaller VC, TV, IC, ERV
Restrictive
- Smaller TLC, VC, IC, TV, ERV, FRC, RV

What is the marker of restrictinon?
Vital capacity - spirometry
What are the lung causes of Interstitial lung diseases?
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis

What are the pleural causes of restrictive lung disease?
Pleural effusion
Pneumothorax
Pleural thickening - asbestos related, pneumonia
What are the skeletal causes of restrictive lung diseases?
Kyphoscoliosis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Thoracoplasty
Rib fractures - soreness
What are the muscular casues of restrictive lung disease?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Obesity - sub diaphragmatic - diaphragm can’t fall properly
Pregnancy - sub diaphragmatic
What is the interstitium?
Space between alveoli and capillary
Between alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium

What is sarcoidosis?
Multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown cause
What is the Histological hallmark of Sarcoidosis?
non-caseating granuloma

What are the clinical signs of sarcoidosis?
Erythema nodosum - granulomas often locate to scar tissue
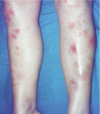
Who gets sarcoidosis?
Adults < 40
Women more than men
World-wide

How do you investigate sarcoidosis?
History and exam
CXR
Pulmonary function tests
Bloods / urinalysis / ECG / TB skin test / eye exam
What would the further assessment of sarcoidosis be?
Bronchoscopy including transbronchial biopsies and endobronchial ultrasound
What would be the different surgical biopsy options for sarcoidosis
Mediastinoscopy
Video assisted thoracoscopic lung biopsy (VATS)
Look at the different stages as presented on these chest X-Rays

When would you provide no treatment for Sarcoidosis?
- Mild disease
- no vital organ involvement
- normal lung function
- few symptoms
When would you treat sarcoidosis with NSAIDS?
Erythema nodosum / arthralgia
When would you treat sarcoidosis with Topical steroids?
Skin lesions / anterior uveitis / cough
When would you treat sarcoidosis with Systemic Steroids?
If Cardiac, neurological, eye disease not responding to topical steroids, or in hypercalcaemia
What is prognosis?
Few Caucasian’s die (<1%)
10-20% get permanent pulmonary/extra-pulmonary complications
Respiratory:
- Progressive respiratory failure
- Bronchiectasis
- Aspergilloma, haemoptysis, pneumothorax
What is the typical presentation for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
- Chronic breathlessness & cough
- Typically 60-70 years old, commoner in men
- Predisposed to lung cancer
- Clubbed & crackles

How does fibrotic tissue vary in the lung?
Usually most prominent in peripheral tissue, central tissue is usually unaffected
Worsens as severity of condition increases
What are the options for Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Median survival 3 y.
- refer to ILD clinic
Medical
- OAF (oral anti fibrotic) – slow down progression but does NOT stop it
- palliative care
Surgical
Transplant


