Clinical anatomy of jaundice 2 Flashcards
Explain the anatomy of the Biliary Tree
Made up of a number of ducts which transport bile
- Right + left hepatic duct = Common hepatic duct
- Common hepatic duct + common bile duct = Common bile duct

How many parts does the doudenum have and where does bil drain into
4 parts
Bile drains into 2nd part
Where is the cystic artery found
triangle for callot - between the common heptatic duct and the cystic duct
Where does the doudenum begin and end
Begins - pyloric sphincter
Ends - Doudenojejunal fleture
Which parts of the doudenum are retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal
- Superior doudenal cap = Intraperitoneal
- Descending = retroperitoneal
- Horizontal = retroperitoneal
- Asceding = Retroperitoneal
What are the secretions of the doudenum
- Gastrin
- CCK
Where does pain form doudenum present
Epigastric region
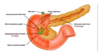
Describe the anatomy of the pacreas
- Locations = right side - lies transversly across poterior abdomen
- Retroperitoneal organ
Parts
- Head - has an uncinate process
- Neck
- Body
- Tail - lies closely to the hilum of the spleen

What are the anatomical relations of the pancreas
Posterioly lies
- Abdominal aorta
- Right and left kidney and adrenal glands
- IVC
- Bile duct
- Superior Mesenteric vessesl
- Part of the portal system
Anteirorly - lies Stomach
Doudenum - surrounds heads
Superior-posterioly - splenic vessels

what do these structure look like on a CT

What are the functions of the pancrea
- Excorine function: Acinar cells - release pancratic digestive enzymes into main pancreatic duct
- Endocrine functions: Islets of langerhands - Releases insulin and glucagon into the blood stream
What is the autonomic supply to the pancreas
Vagus nerve (all glands are supplied by parasympathetics
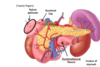
How does drainage from the biliary system occur
- Bile duct descends posteriorly to the 1st part of doudenum
- Then travels into a groove on the posterior aspect of the pancreas
- Bile duct joins with the main prancreatic duct to form the ampulla of vater- wider duct
- both drain Into the major doudenal papilla in 2nd part of doudenum
there are 2 papillas in the 2nd part of the doudenum what are they and what do they drain
- Major papilla - drains ampulla of vater
- Minor papilla - drains accessory pancreatic duct
What are anatomical sphicter
areas of lumen where smooth muscle encircles the lumen of the tract
What are the sphincters related to secretion into the doudenum
- Dile duct sphincter
- Sphincter of oddi
- pancreatic sphincter

What do the ducts look like on ERCP
procedure to looks at the different ducts - Biliary tree and pancreas to treat pathologies within it
- Endocope intersted into oral cavity into doudenum
- Cannula placed into major doudenal papilla and radio-opaque due is injected back into biliary tree
- Radiographic images are then taken

What are the causes post-heptic jaundice
- Gallstones
- Carcinoma of head of pancreas
- causes flow of bile and bilirubin back into liver

What is the blood supply to the doudenum and pancreas
- Superior peancreatic doudenal artery - branch of gastrodoudenal artery
- and inferior panctreatic doudenal artery - branch of superior mesenteric artery
- Anastomosis at head of pancreas
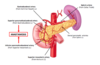
At what level does the superior mesenteric artery branch come off the aorta
L1
What is pancreatic pain and where is it felt
- Pancreatitis due to Gallstone blockage of ampulla- Bile diverted to pancrea - irritation and inflammation
- Midgut and foregut structure
- Epigastric region
- Umbillicul region
- Back radiation
What us acute pancreatitis

is the small intestine a foregut or mid-gut structures
- 1st and second part of doudenum - foregut
- Rest of small intestine - midgut
Describe the anatomy of the jejunum and ileum
- Most of the small intestines
- Found in all 4 quadrants

Where does jejunum begin and ileum end
- jejunum begins - Doudenaljejunal flexure - Intraperitoneal
- Illeum ends at - Ileocaecal junction

What is the difference in jejunum and ileum
What is the blood supply to the jejunum and ileum
Aterial blood supply
- Suprior mesenteric artery branches
- Jejunal and ileal arteries
Venous drainage
- Jejunal and ileal veins
- to supeiror mesenteric veins
- To hepatic veins

Describe the anatomy of the superior mesenteric vessels
- leave aorta at L1
- Posterior to the neck of pancreas
- Travels inferior, anerior to the uncinate process of the pancrease to enster the mesentery proper

How is absorption of fat carried out
- Bile help to absorb fat from GI lumen into the intestinal cells
- Fat with chylomicrons are then absorbed from the intestinal cell into specialised lymphatic vessels of the small intestine called lacteals
- They travels via the lymphatic system to eventually drain into the venous system at left venous angle
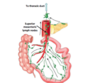
Describe the lympahtics of the abdomen
- Lie along side arteries
Main groups drianing abdominal organs:
- Celiac nodes - foregut
- Superior mesenteric nodes - Midgut
- Inferior mesenteric nodes - hindgut
- Lumbar nodes - kidney, posterior abdominal wall, pelvis and lower limbs
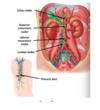
What is the venous angle
junction between Sub-clavian and internal jugular veins
- Left venous angle - thoracic duct drainage
- Right venous angle - right lymphatic duct drainage



