Classification of Amino Acids Flashcards
(28 cards)
Structure of Amino Acids

Acidic AAs
- Aspartic Acid
- Glutamic Acid
Aspartic Acid
Asp, D
aspartate - the anionic/deprotonated form
(how this amino acid is observed at physiological pH)

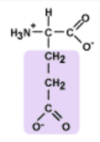
Glutamic Acid
Glu, E
glutamate - the anionic/deprotonated form
(how this AA is observed at physiological pH)
Basic AAs
- Lysine
- Arginine
- Histidine
Lysine
Lys, K
pKa = 10
cationic/protonated at physiological pH

Arginine
Arg, R
pKa = 12 at physiological pH
cationic/protonated at physiological pH

Histidine
His, H
pKa = 6.5 at physiological pH
can either be protonated (acidic) or deprotonated (basic)

Hydrophobic (Nonpolar) AAs
- Glycine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
Characteristics of Hydrophobic/Nonpolar AAs
- either have aliphatic or aromatic side chains
- hydrophobic residues tend to associate with each other rather than with water
- therefore are found on the interior of folded globular proteins, away from water
- the larger the hydrophobic group, the greater the hydrophobic force repelling it from water
Glycine
Gly, G
aliphatic side chain

Alanine
Ala, A
aliphatic side chain

Valine
Val, V
aliphatic side chain
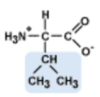
Leucine
Leu, L
aliphatic side chain

Isoleucine
Ile, I
aliphatic side chain

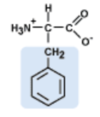
Phenylalanine
Phe, F
aromatic side chain
Tryptophan
Trp, W
aromatic side chain

Polar AAs
- Serine
- Threonine
- Tyrosine
- Asparagine
- Glutamine
Characteristics of Polar AAs
- R-group is polar enough to form H-bonds but does not act as an acid or base
- are hydrophilic, that is they interact with water whenever possible
Serine
Ser, S

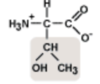
Threonine
Thr, T
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y

Asparagine
Asn, N
the amide derivative of aspartic acid

Glutamine
Gln, Q
the amide derivative of glutamic acid






