Chest Xray Interpretation Flashcards
(45 cards)
What should the cardio-thoraic ratio be?

Cardio-Thoracic Ratio (CTR) should be <50% on a PA (posterior-anterior i.e. back to front) image*
CTR- heart size should be half the width of the chest
Further away something is from detector, ——— the image.
Image is enlarged
Don’t want the heart to be magnified, so stand with chest to detector.
How many lobes are there on each lung

Which bronchus do inhaled foreign bodies tend to go down
Right Main Bronchus
slightly wider, shorter and more vertical
What might a patient be asked to aspirate prior to a chest CT
Aspirate barium into lungs prior to CT to highlight pathologies.
What is the hilar
‘Lung roots’, they anchor the lungs/heart/great vessels. Seen as fuzzy densities either side of the midline.
The ——– hilum is commonly higher than the ———, due to the pulmonary artery
The left hilum is commonly higher than the right, due to the pulmonary artery
Changes in density, size or positioning of the hilar is highly indicative of abnormality
Give two diseases where the hilar may be enlarged
- Lymphadenopathy (calcified show on X-ray) and tumours
- Pulmonary venous hypertension (LVF, mitral stenosis or mitral reflux)
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension (primary pulmonary hypertension and lung diseases such as COPD)
- Increased pulmonary blood flow
Which pleura doesn’t contain pain receptors
- Visceral Pleura (inner-no pain receptors)
Describe the three pleural layers
- Visceral Pleura (inner-no pain receptors)
- Parietal Pleura (outer- attached to chest wall & sensitive to pain)
- Pleural space between pleura contains lubrication
True or False: Lung markings should reach the thoracic wall
True
True or False: The hemidiaphragms are not at the same level.
True
The right hemidiaphragm is commonly higher than the left by —— intercostal rib space height (~2 cm) as sitting on top of ——
The right hemidiaphragm is commonly higher than the left by one intercostal rib space height (~2 cm) as sitting on top of liver.
When one hemidiaphragm is significantly higher than the other (>3cm) an abnormality is likely
Gastric air bubble in stomach seen on ——- side (common, no pathology)
On ——side = pathology.
Gastric air bubble in stomach seen on left side (common, no pathology), on right side = pathology.
The bones visible in the chest radiograph include
- Ribs
- Clavicles
- Used to assess positioning of chest x-ray
- Scapulae
- Vertebrae
- Proximal humeri
When may a nasogastric tube be used
NG tube is used for short- or medium-term nutritional support i.e. oesophageal cancer or stroke (loss of gag reflex)
Purpose of endotracheal tube
Inserted into the trachea to establish and maintain a patent airway
When may a central venous catheter be used
Need centrally given drugs- peripheral not adequate
When may a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC line/catheter) be used
Intravenous access for a prolonged period (e.g., chemotherapy, extended antibiotic therapy, or total parenteral nutrition)
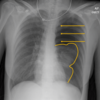
What is this abnormality

Pneumothorax
What is a pneumothorax
- Air trapped within the pleural space
- Pushes the visceral membrane away from the chest wall- so see the border of the visceral membrane (white line)
- Clearly defined line paralleling the chest wall
- Upper part of the line is curved at the apex
- Absence of lung markings
3 types/causes of pneumothorax
- Primary spontaneous
- Secondary spontaneou
- Trauma
What is a Subpleural bleb
- small out-pocket/bulge in lung but can rupture and release air into pleural space, causing pneumothorax
In some cases, intra-pleural air volume will increase, exerting pressure on the mediastinal and intra-thoracic structures.
What is the name of this medical emergency?
Tension Pneumothorax