Chest Radiology Slides Flashcards
(17 cards)
What imaging views are shown here?

left: posterior-anterior (PA) view
right: lateral view

- ascending aorta
- Right Atrium
- aortic arch
- aortopulmonary window
- left ventricle

Atelectasis
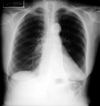
an entire lobe of the lung has lost its air, causing all alveoli it that lobe to collapse
- *- Sail sign
- Less alveolar surface =**
Hypoxia, Decreased Lung Volume, normal CO2
Atelectasis

When lungs lose volume, other structures move in, in this case, the left diaphragm
Localized, round opacity
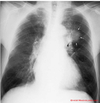
tumor + enlarged lymph nodes
PULMONARY EDEMA

Interstitial fluid thickens the spaces between the alveoli and causes their collapse. Typical batwings (or butterfly) shape
What is wrong in this image?

COPD
- The lung fields are stretched and compress the mediastinum; the diaphragm is pushed down
- Many alveolar sacs have ruptured and formed blebs, which do not contribute in the air exchange
- less alveolar surface = carbon dioxide exchange is reduced and patients retain CO2
Emphysema, asthma, chronic bronchitis + GERD
COPD plus pneumonia

Constant production of mucus and irritation of the airways can result in obstruction and infection
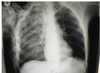
What is wrong?

pneumothorax
(Air in the pleural space)
Tension Pneumothorax

- The free air around the lungs occupies space and compresses the mediastinum.
- This impedes venous return to the heart
THIS IS AN EMERGENCY!!!!!
What’s wrong with this?
Rib Fractures with pulmonary contusion
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
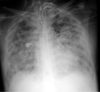
- Trauma
- aspiration pneumonia
- sepsis
initiate an acute process of lung destruction
(here you see it as Patchy Infiltrates)
Empyema

Pus within the pleural space outside lung
Pulmonary abscess

Pus within the lung parenchyma inside lung
Pericardial Effusion

Fluid around the heart, but inside the pericardium
What does this show (or not show..)?
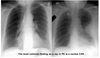
Pulmonary Embolism
- Blood clot in vessels of lung
(Hampton’s hump = part of lung is devoid of air; it collapses)
What is shown in this CT Angiography (CTA) ?

Pulmonary Embolism


