Chemical Reactions: Reactants, Products and Energy Change Flashcards
Define chemical reaction.
A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.
What do chemical reactions involve?
The breaking and formation of chemical bonds.
What can chemical reactions be represented by?
Chemical equations.
Examples of chemical reactions.
Burning Magnesium Iron rusting Acid dissolving Copper Oxide
Define chemical equation.
A symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using formulae.
How are chemical equations set out?
Reactants appear on the left side and products on the right with them separated by an arrow.
Examples of chemical equations.
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ➝ NH₃(g)
2Mg(s) + O₂(g) ➝ 2MgO(s)
What do balanced equations indicate?
The relative numbers of particles (atoms, molecules or ions) involved in the reaction.
Define reactants.
The starting materials for a chemical reaction that appear to the left of the arrow in an equation.
Define products.
The substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction that appear to the right of the arrow in the equation.
Define phase change.
A physical change where a substance changes between the solid, liquid, gaseous or aqueous state. Also called a change of state.
Examples of phase change.
Water freezing
Mercury boiling
Salt dissolving
Labelled chemical equation diagram

Define enthalpy (H).
The stored chemical potential energy in a substance (often called the heat content).
What do reactions often involve?
A change in enthalpy
∆H = Hproducts - Hreactants
Example of enthalpy.
Combustion of Ethanol
∆H = -1370kJ
Law of conservation of energy.
The total amount of energy within a system remains constant (is conserved), although the energy within the sysem can be changed from one form to another.
Example of the law of conservation of energy.
Combustion of Ethane.
Energy is released as heat but only because the products have less chemical energy than the reactants.
Law of conservation of mass.
In a closed system mass will remain constant over time.
Mass will only change if matter is added or removed.
Mass (and energy) can neither be created nor destroyed.
Example of the law of conservation of mass.
H2 + O2 → 2H20
4g 32g 36g
Define exothermic reaction.
A reaction where the system realeases energy to the surroundings (as heat).
The reactants have more energy than the products and the exess is released as heat.
Equation for exothermic reactions.
∆H = -ve
Examples of exothermic reactions.
Burning coal
Adding acid to water
Mg combusing
Water freezing
Define endothermic reaction.
A reaction where the system absorbes energy from the surroundings (as heat).
The products have more energy than the reactants.
Equation for endothermic reactions.
∆H = +ve
Examples of endothermic reactions.
Cracking an ice-pack
Dissolving NH4NO3 in water
Boiling water
States of matter.
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Aqueous solution
Change in state during condensation.
Gas to liquid
Change in state during boiling.
Liquid to gas.
Change in state during evaporation.
Liquid to gas (<bp></bp>
Change in state during freezing.
Liquid to solid.
Change in state during melting.
Solid to liquid.
Change in state during sublimation.
Solid to gas.
Change in state during deposition.
Gas to solid.
Define latent heat of fusion.
Energy required to change state from solid to liquid.
Define latent heat of vaporisation.
Energy required to change state from liquid to gas.
Define boiling point.
Temperature at which vapour pressure of liquid = pressure outside liquid.
Define melting point.
Temperature at which solid changes to liquid at atmospheric pressure.
Define mole.
Avogardro’s number of particles.
6.02 × 1023
Define Avogadro’s Number (N).
The number of atoms in 12.01 grams of Carbon 12.
1 mol = Avogadro’s Number = 6.02 × 1023
Number of moles formula in relation to Avagadro’s number.
n=number of moles
N=number of particles
NA=Avagadro’s Number (6.02 × 1023)

Number of moles formula in relation to mass.
n=number of moles
m=mass (g)
M=molar mass (g/mol-1)
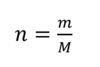
Number of particles formula.
N=number of particles
n=number of moles
NA=Avagardo’s number (6.02 × 1023)

Mass formula.
m=mass (g)
n=number of moles
M=molar mass (g/mol-1)

Molar mass formula.
M=molar mass (g/mol-1)
m=mass (g)
n=number of moles

How to calculate mass to mass relationships.

Define limeting reagent?
The reactant that is used up first.
Define exess reactant?
The reactant that is in exess.
Define the left over?
A substance in limiting reagent problems that is left over from the exess.
Left over formula.
n(left over) = n(start) - n(reacted)


