CHEM4: Antiprotozoan Bioreductive Nitroimidazoles Flashcards
What are nitroimidazoles?
Bioreductive prodrugs
Cytotoxic to anaerobic microorganisms + hypoxic eukaryotic cells

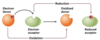
What is a REDOX reaction?
Coupled reaction that occur when a transfer of electrons takes place
Oxidation = loss of electrons
Reduction = gain of electrons
Most biochemical transformations = redox reactions.
Give examples.
-
Cellular respiration
- In cellular respiration, glucose = oxidised to carbon dioxide
- Molecular oxygen = ultimate electron acceptor
- C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy
- Drug metabolism
-
Photosynthesis
- Carbon dioxide = reduced to sugars
- water = electron donor
- 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
What mediates biological redox reactions?
Redox enzymes (oxidoreductase)
These enzymes use coenzymes (NAD + NADP) as electron carriers
Most redox reactions = stereoselective because the reactants are bound by enzymes in predetermined + fixed spatial relationships

What is an oxidation state?
An indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound
Also the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elemts were 100% ionic
- Increase in OS = oxidation
- Decrease in OS = reduction
What is the OS of a free element (uncombined)?
0
What is the OS of a simple (monoatomic ) ion?
OS = equal to the net charge on the ion
What is the OS of hydrogen _ oxygen>
hydrogen = 1
oxygen = -2
The algebraic sum of oxidation states of all atoms in a neutral molecule must be _____, while in ions the algebraic sum of the oxidation states of the constituent atoms must _____
§The algebraic sum of oxidation states of all atoms in a neutral molecule must be zero, while in ions the algebraic sum of the oxidation states of the constituent atoms must be equal to the charge on the ion.
The _____ the oxidation state of a given atom the _____ its degree of oxidation; the _____ the oxidation state the _____ its degree of reduction.
The higher the oxidation state of a given atom the greater its degree of oxidation; the lower the oxidation state the greater its degree of reduction.
Provide examples of how to calculate OS
Burning hydrogen in air
- oxidation of hydrogen to water
Tollen’s test for the presence of aldehydes
- oxidation of aldehyde to carboxylic acid with silver ions
What are ferredoxins?
Iron (fer-) containing redox (-redox) active proteins
Participate in redox reactions, it is an inorganic source + sink of electrons
Contain iron-sulfur clusters which are redox-active
Iron-sulfur clusters are found in ancient + conserved proteins + ancient minerals
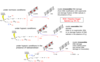
Describe the cellular actions of nitroimidazoles
Under anaerobic conditions (as they occur in protozoans and some bacteria):
- Nitroimidazoles (R-NO2) diffuse into cells and are reduced to nitro radical anions.
- In protozoans (and bacteria) nitroimidazoles are reduced by ferredoxin, whose oxidation is coupled to pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR).
- Further reduction leads to the nitrosoimidazoles. Nitro radical anions and nitroso compounds are highly reactive and cause oxidative damage to DNA (genotoxicity, mutation) and other cellular components, leading to cell death
Under aerobic conditions (as they occur in mammalian host cells):
- O2, the best cellular electron acceptor, oxidises the nitro radical anions back to the nitro form.
- In this process, O2 is reduced to superoxide, which is scavenged by superoxide dismutase (SOD). This is called futile cycling. Depending on [O2], cell death is reduced or avoided.

Every redox reaction consist of 2 half reactions.
What are these half reactions expressed as?
Reductions
Each half reaction has a reduction potential E0
E0 = how easy a substance loses electrons
How do we determine if a redox reaction will occur?
We compare E0 values of the half reactions
- the component with the more –ve E0 will donate electrons;
- the component with the more +ve E0 will accept electrons;
- the more negative E0 for a half-reaction, the further the equilibrium position lies to the left.
- E0 net is the sum of the E0 values of the half reactions (invert sign if half reaction occurs in opposite direction) and can be used to assess how (un)favourable a redox reaction is. If E0net > 0, reaction is spontaneous.

Biological reduction of nitroimidazoles

Describe radiotherapy + how it needs oxygen for its function?

How can nitroimidazoles be used as radiosensitisers?