Chapter 9 Flashcards
(113 cards)
What is the most common cause of rhinitis (sneezing, congestion, and runny nose)?
Rhinovirus
What causea allergic rhinitis?
Type I hypersensitivity (e.g. to pollen) characterized by an inflammatory infiltrate with eosinophils
What are the most common causes of nasal polyps?
Usually secondary to repeated bouts of rhinitis,
also occur in cystic fibrosis and aspirin-intolerant asthma

What is the classic triad of aspirin-intolerant asthma?
asthma, aspirin-induced bronchospasm, and nasla polyps
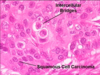
What is this?

Benign tumor of nasal mucosa composed of large blood vessels and fibrous tissue; classically seen in adolescent males
Presents with profuse epistaxis (nosebleeds)
What is nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
A MALIGNANT tumor of nasopharyngeal epithelium associated with EBV

Who commonly gets nasopharyngeal carcinomas?
Chinese adults and African children
Describe the histo of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Pleomorphic keratin-positive epithelial cells in a background of LYMPHOCYTES

What is the most common cause of epiglottitis?
H. influenzae type B (esp. in nonimmunized children)
How does epiglottitis present?
High fever
sore throat, drooling with dysphagia, muffled voice
inspiratory stridor
What is the most common cause of laryngotracheobronchitis (croup)?
Parainflunzae virus
What is the most common cause of laryngotracheobronchitis (croup)?
Parainflunzae virus
How does croup present?
Hoarse, ‘barking’ cough and inpiratory stridor
What is this?

Vocal cord nodules (usually bilateral)- due to excessive use of the vocal cords and presents on the TRUE vocal cords
Composed of myxoid CT

What is this?

Laryngeal papilloma- a BENIGN papillary tumor of the vocal cord due to HPV 6 and 11 (single in adults and multiple in children)
Presents with hoarseness
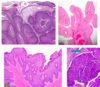
What are laryngeal carcinomas?
Squamous cell carcinoma usually arising from the epithelial lining of the vocal cords

What are the risk factors for laryngeal carcinomas?
alcohol and tobacco- can rarely arise from a laryngeal papilloma
Presents with hoarseness, cough, and stridor
What is pneumonia?
Infection of the lung parenchyma that typically occurs when normal defense mechanisms are impaired (e.g. impaired cough reflex, damage to the epithelium)
How does pneumonia present?
Fever and chills, productive cough with yellow-green or rusty (bloody) sputum, tachypnea with plueritic chest pain, decreased breath sounds, dullness to percussion, and elevated WBC count
What are the major patterns of pneumonia?
Lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial
What is lobar pneumonia?
Marked by consolidation of an entire love of the lung
What are the most common causes of lobar pneumonia?
Usually bacterial, most commonly Strep. pneumoniae (95%) and Klebsiella
What are the histologic phases of lobar pneumonia?
- Congestion- due to congested vessels and edema
- Red hepatization- due to exudate, neutrophils, and hemorrhage filling the alveolar spaces
- Grey hepatization- due to degradation of red cells within the exudate
- Resolution

What stage of lobar pneumonia is this?

Red hepatization