Chapter 7 - Nitrogen Compounds Flashcards
Define an amine
central nitrogen with 3 sigma bonds (to either hydrogen or carbon) and a lone pair
Imine structure

Secondary amine structure

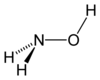
Hydroxylamine structure
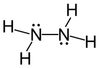
Hydrazine structure
Oxime structure

What is the base strength (pKb) of amines?
They are weak bases.
pKb between 3 and 5
Which amine substitution is most basic? Why?
secondary amine: alkyl group substitution affects sterics (makes it more hindered), but is balanced by the inductive effect (donates greater electron density)
Equation: equilibrium constant for proton-transfer reactions
Keq = 10pKa(product acid) - pKa(reactant acid)
Equation: Henderson-Hasselbalch pH
pH = pKa(protonated species) + log [deprotonated species]/[protonated species]
Do alkoxy groups donate or withdraw electron density by resonance?
They donate electron density.
What is the product of ammonia reacted with an alkyl halide?
tertiary amine (maybe quaternary)
Amines tend to undergo multiple additions with alkyl halides.
What is formed when an amine reacts with an ester?
amide
What is formed when an amine reacts with a carboxylic acid?
amide
How does aromaticity affect basicity?
Since electron density is tied up in the aromatic ring, it is less available for donation, reducing the compounds basicity.
What is formed when an amide is reacted with LiAlH4?
It is reduced to an amine.
What is formed when an imine is reacted with NaBH4?
It is reduced to an amine.
For reactions of amines, what are two general results?
Either:
- leaving group is displaced
- water is formed as a side procuct
What happens in a Hofmann elimination reaction?
A primary amine is reacted with excess methyl iodide, forming a quaternary amine cation. When reacted with Ag2O and heat, it undergoes E2 elimination, kicking the tertiary amine off, and forming a less substituted alkene.
Is an aldehyde or ketone more electrophilic?
aldehyde is more electrophilic
What is formed when a primary amine is reacted with an aldehyde/ketone?
imine + water
With what compounds does an amine tautomerize?
enamine
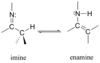
What is formed when a secondary amine is reacted with an aldehyde/ketone?
enamine
As amides become increasingly substituted, how does this affect the compound’s boiling point?
Boiling point is lowered with increasing substitution, because the hydrogens on an amide nitrogen can hydrogen bond with the oxygen on the carbonyl.
What is formed in a Hofmann Rearrangment?
A primary amide rearranges to form a primary amine and carbon dioxide.
Naturally occuring amino acids have what stereochemistry at carbon 2? What is an exception?
S-stereochemistry (except cysteine has R). All of these are L.
What is the pKa of the side chain in lysine?
10.8
What is the pKa of the side chain in aspartic acid?
3.9




