Chapter 4 Whole Body Flashcards
Abdominal Cavity
The cavity beneath the thoracic cavity the aid separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm

Abdominopelvic Cavity
A term that describes the abdominal and pelvic cavity, refers to the space between the diaphragm and the groin

Anaplasia
A change in the structure and orientation of the cells, characterized by a loss of differentiation and reversion to a primitive form
Anatomical position
The standard position for the body as a whole, standing arms/palms forward

Anterior
Pertaing to the front of the body towards the belly of the body

Aplasia
A developmental failure resulting in the absence of any organ or tissue
Cardiac Muscle
The muscle that makes us the muscular wall of the heart
Caudal
Pertaining to the tail
Cell
The smallest and most numerous structural unit of living matter

Cell membrane
The semipermeable barrier the is the outer covering of a cell

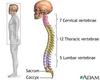
Cervical Vertebrae
The first seven segments of the spinal colum, identified as C1 through C7

Chromosomes
The threadlike structures within the nucleus that controls the functions of growth, repair, and repoduction for the body

Coccyx
The tail bone
Connective Tissue
Tissue that supports and binds other body tissue and parts
Cranial
Pertaining to the skull or cranium
Cranial Cavity
The cavity that contains the brain
Cytology
The study of cells
Cytoplasm
A gel like substance that surrounds the nucleus of a cell.

Deep
Away from the surface and towards the inside of the body
Distal
Away from ot farthest from the trunk of the body or farthest from the point of origin of a body part

Dorsal
Pertaining to the back

Dorsum
The back or posterior surface of a part; on the foot, the top of the foot
Dysplasia
Any abnormal development of tissues or organs
Epigastric Region
The region of the abdomen located between the right and left hypochondriac regions in the upper sactions of the abdomen, beneath the cartilage of the ribs





























