Chapter 2 - The Market Mechanism Flashcards
What is microeconomics?
Microeconomics is the branch of economics that looks at the behaviour of the small economic agents that make up the whole economy.
What is a market?
A market is seen as any place that allows buyers and sellers to interact and exchange goods and services.
What is a competitive market?
A competitive market is one where there are a large number of buyers and sellers and each of them has little influence on the prices’s (referred to as price-taking).
What is a consumer surplus?
It is the difference between the price the consumer is willing to pay and market price.

What is producer surplus?
When producers sell the product above their economic cost (including opportunity cost)

What is the Market Mechanism?
describes how the forces of demand and supply determine relative prices of goods and services.
Describe the law of demand.
- as prices increase, the quantity demanded decreases
- as prices decrease, the quantity demanded increases
What are the 2 main effects on demand?
(they also support the law of demand!)
- Income effect: some people will not be able to afford the products prices rise. At a lower price, we can afford more of a goods or service.
- Substitution effect: when the price of one good increases, consumers will look towards cheaper substitutes; so quantity demanded of the original product is likely to fall.
Describe movement along the demand curve
Movement along the demand curve is only** due to a change in the products **price
- demand contracts, when prices increase
- demand expands, when prices decrease
Describe movement of the demand curve
A shift of the entire demand curve will occur when one of the factor of demand’s, other than price has changed
Demand-Side Factor: Disposable Income
Disposable Income is defined as the total income that households have received in exchange for their participation in the production process plus government transfers less direct (income) taxes.
Increase in disposable income will lead to an increase in demand for normal goods
Demand-Side Factor: change in interest rates
Increased interest rates = less discretionary income thus a decrease in demand.
decreased interest rates leads to an increase in demand.
Demand-Side Factor: Price of Substitutes
- A substitute is a viable good or service that may be used instead of the product in question
- Cheaper Substitutes = less demand for original good
Demand-Side Factor: Price of Complements
Complementary products are generally consumed together.
i.e. a decrease in the price of ipods = an increase in demand for itunes music.
Demand-Side Factor: Preferences and Tastes
demand may be affected by an individual’s tastes, attitudes and preferences towards each good or service
Demand-Side Factor: Population growth and demographic change
- A growing population consumes more goods and services
- Structure of a population affects the range of goods and services that are sold in the market.
Demand-Side Factor: Consumer Sentiment (confidence)
Consumer sentiment is the measure of the general expectations about the future state of the economy.
This will affect marginal propensity to consume which measures the change in consumption that would result from a one dollar increase in income.
What is the law of supply?
Law of Supply
- as prices rise, the quantity supplied increases
- as prices fall, the quantity supplied falls
This is because:
- a higher price represents a higher profit
- a higher price increase the opportunity cost of using resources elsewhere
- to increase production, cost per unit might increase
What is movement along the supply curve?
Movement along the supply curve is only due to a change in the products price
- when prices increase, supply expands
- when prices decrease, supply contracts
What are the factors that effect the movement of the supply curve.
(supply side factors)
If the supply curve shifts to the right this means that for each given price, there is a greater quantity supplied (and vice-versa). Below are the factors that affect a supply curve:
- Prices of the factors of production: every good and service requires resources. Common costs associated with these are; wages/salaries, costs of tech, rent, utility bills…
- Price of other products: the opportunity cost of producing product X compared to product Y
- Technological Change: new tech will generally increase the productivity of existing resources.
- Climate: most G+S rely upon nature for the provision of raw materials. Therefore, climate disruptions can have a major effect on a suppliers ability or willingness to supply.
What is equilibrium price?
When one price at a moment of time, satisfies buyers and sellers, and the price at which the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied at the time.

Higher demand Graph

Lower demand Graph

Lower Supply Graph & Higher Supply Graph.

What is resource allocation?
Resource allocation is the study of how resources such as land, labour, capital are used to produce goods and service to meet the needs of households, businesses, governments and other economic agents.
What is the ‘value’ of a good or service?
The value of any good or service is determined by the buyers willingness to pay relative to its availability.
What is relative prices?
Seen as the price of any one good or service measured in the terms of the price of another good or service.
How are the 3 key economic questions answered in a market-based economy?
- What to produce is answered by the market mechanism, which will allocate resources to those goods and services in high demand. Consumers are the main driver in a market-based economy.
- How to produce is answered by the price mechanism which describes how the forces of demand and supply determine relative prices of goods and services, which then ultimately determine the way our productive resources allocated in the economy.
- For whom to produce is determined by the potential customers willingness and ability to pay.
What is PED?
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
= percentage change in QTY demanded ÷ percentage change in PRICE
What is HIGH, LOW and UNIT PED?
- High PED (elastic): product will have high PED if value is greater than 1. In this situation the percentage change in quantity demanded will be greater than the percentage change in price. Demand curve is flat.
- Low PED (inelastic): product will have low PED if the value is less than 1. In this situation, the percentage change in quantity demanded will be less than the percentage change in price. Demand curve is steep.
- Medium PED (unit elastic): elasticity value will equal 1. Percentage change in quantity demanded and price are equal.
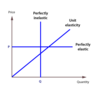
What are the factors affecting price elasticity of demand?
- Degree of necessity: goods and services deemed necessities will usually have a low PED whereas luxury products will have a relatively high PED.
- Availability of substitutes: the greater the number of substitutes that are available for a product the greater the PED. Consumers are likely to switch to a close substitute if prices rise.
- Proportion of Income: the greater the percentage of income that is needed to purchase a good or service, the greater the PED.
- Time: consumers have a habitual buying behaviour, meaning they are less likely to notice price changes in the short term. Overtime however, consumers may notice prices increase and experiment with alternative products.
What is PES?
- Price Elasticity of Supply (PES) looks at the responsiveness to changes in supply when price changes.
PES = percentage in QTY supplied ÷ percentage change in price

What are the factors affecting price elasticity of supply?
- Production Period: as prices increase, firms may wish to increase their supply, but it will take time to shift resources from the production of other goods and services.
- Spare Capacity: if a firm has spare capacity then it is more likely to respond to changing prices.
- Durability of Goods: if goods can be stored, then it will be much easier to respond to changing prices.
What are the demand-side factors?
- Disposable Income
- Change in interest rates
- Price of Substitutes
- Price of complements
- Preferences and Tastes
- Polulation Growth and Demogrpahic Change
- Consumer Sentiment (confidence)


