Chapter 2: Plate Techtonics Flashcards
(23 cards)
Earth’s “puzzle” pieces
Crustal plate boundaries
What were Alfred Wegener’s ideas about continental drift?
What was the problem with his ideas?
Came up with idea that continents had “drifted” apart in 1915. They were thought to slide across a stable and ancient oceam floor. Suggested there was once a “supercontinent” that he termed “Pangaea” (all lands).
Problem: Wegener had no mechanism for “drift of the continents”.
Pangaea
“Supercontinent” that existed ~200 million years ago
What are the units/terminogoly used for age?
a = annum (100 = 1 year) .
ka = Thousand years (103=1,000)
Ma = Million years (106=1,000,000)
Ga = Billion years (109=1,000,000,000)
____________________________________________
kya = Thousand years ago
Mya = Million years ago
Gya = Billion years ago
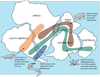
What was the primary evidence Wegener noted for Pangaea’s existence?
The following features matched on all continents, now separated:
- Fossils (ex. Mesosaurus fossils, see image attached)
- Rock types/ages
- Similar geologic structures
- glacial deposits
What kind of trace to glaciers leave, if any?
They scour the landscape leaving evidence of their existence and path.
Glacial deposits indicate ide flow away from a central location (south pole).
Who created the first profiles of the seafloor in the pacific and how?
Harry Hess when he left echo sounder on during WWII transits.
What does magnetic mapping do?
Measures the rate of seafloor spreading.

Where on the ocean floor are the youngest and oldest points located?
Youngest points (0 Ma) are at very long topographic highs.
Oldest are at the edges, frequently at trenches (oldest ocean floor is ~200 Ma).
Continental rocks up to 4 Ga (billion years)
How many major plates is the Earth’s outer shell made up of?
13
Where is the Ring of Fire and what is it’s significance?
IT is between the Indo-Australian Plate, Eurasian Plate, North American Plate, Cocos Plate, and Pacific Plate.
It’s an area where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean. Home to over 75% of world’s active and dormant volcanoes.

What are the keys for convection?
Heat source at one end
Thermally expansive
Gravity
Fluid response (viscous)
What are the driving mechanisms for plate motions?
Destructive margins, or “subduction zones”
Constructive margins, or “mid-ocean ridges”
What are the 3 major types of plate boundaries?
Divergent or Constructive (mid-ocean ridges)
Convergent or Destructive (subduction zones)
Conservation or Transform margins (tranform faults)

What happens during ocean-ocean convergence and what usually forms after?
Two oceanic slabs converge and one descends beneath the other, often forming volcanoes on the ocean floor then volcanic island arcs.
Example: Aleutian, Mariana, Tonga Islands.
What is ocean-contingent convergence and what results?
Collision between an ocean and continent. Oceanic plate will subduct beneath the continents and volcanic arcs form on continents.
Exampls: Pacific NW, Andes, Japan.
What is continent-continent convergence and what results?
Collision between two continents (one subducts beneath the other) and produces large mountain ranges.
Ex: Himalayas (collision of India and Asia) and Appalachians.
What do diverging oceanic plates produce?
Oceanic ridges along well-developped boundaries, forming from mantle upwelling. Along ridges seafloor spreding creates new seafloor.
What are divergent continental plate boundaries and what is an example of an area that is currently experincing this?
Continental rifts form at spreading centers within a continent. Rio Grande Rift is opening.
Ex: East African Rift
Define Transform plate boundaries and give example
Plate slide past one another, no new crust is formed/destoyed, most join two segments of a mid-ocean ridge.
Roughly parallel the direction of plate movement.
Ex: San Andreas Fault in CA
Define Mantle Plume.
Mantle plumes originate deep within the asthenosphere as molten rock which rises and melts through the lithospheric plate forming a large volcanic mass at a “hot spot”.

Coral Reefs and Atoll formation.

How do we measure present-day plate motion?
Global Positioning Systems (GPS).


