Chapter 2 - Major Airframe Components Flashcards
(21 cards)
What are the 3 types of joining methods?
Permanent (riveting, adhesives)
Non-permanent (bolting)
Transitional (Pinning, speed tape)
What are blind rivets?
Rivets used when access can only be gained to one side of the structure
What is a lock wire?
A permanent fixing part of a set of bolts.
The only way to get one off is to destroy it.
What are some different construction techniques?
Truss
Monocoque
Semi-monocoque
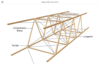
What are the features of a truss structure?
Carries tension and compression loads
Wire braced
longerons provide stiffness
What are the features of a monocoque structure?
series of aluminium frames joined by longerons
Metal skin attached around the whole assembly
no internal framework
Skin is partly structural so damage will weaken structure

What are the features of a semi-monocoque design?
Skin is only for aerodynamic shape
formers/frames define shape
stringers run longitudinally and help withstand buckling
longerons are the main structural load carrying members
bulkheads provide structural partitions inside fuselage
firewalls are fire resistant bulkheads

What is a machined or integral structure and what are the benefits?
Where a single piece of aluminium is machined so that it forms and skin and stringer like structure
there are no need for rivets and therefore it saves weight and is good for wet wings (fuel tanks)

Why is a fuselage usually circular?
This prevents airflow separation and it is easier to absorb loads from pressurisation
What are the benefits and drawbacks to an oval fuselage cross section?
Benefits:
lower manufacturing costs; greater capacity so increased revenue; better options for cargo loading and unloading.
Drawbacks:
Less ability to withstand hoop loads
What is the maximum that a cabin is usually pressured to?
8 or 9 psi
What are the purpose of blow out bungs?
if the pressure differential between the cabin and the cargo bay is too high then the bungs will blow out allowing for equalisation.
Where do the TE flight controls attach?
The rear spar
Where do the LE flight controls attach?
The front main spar.
What are the 3 types of wing design?
Cantilever
semi-cantilever
externally braced
What is the difference between a cantilever wing and a semi-cantilever wing?
the semi-cantilever wing has struts the extend from the fuselage to a point along the wing.
Why don’t high speed jet transport A/C have semi-cantilever wings?
Struts create too much drag
What is the normal shape of the main wing spar?
An I beam
What is a torsion box?
A section created with spars linking together to form a very rigid, resistant to twisting section, which adds to wing strength.
What are the purpose of wing ribs?
to provide aerodynamic shape; allow stressed skin to be attached; transfer loads to the spars.
What is a wet wing?
Wing spaces that allow for storage of fuel.


