Chapter 18: Hepatic Disease Associated with Pregnancy Flashcards
Hepatic diseases may occur in women with chronic liver disease who become pregnant, or they
may develop during pregnancy in women who were not affected by liver disease.
Abnormal liver
tests occur in 3% to 5% of pregnancies. [68]
What is the most common cause of jaundice in pregnancy?
Viral hepatitis (HAV, HBV, HCV, and even HBV +
HDV)
While these women require careful
clinical management, pregnancy does not specifically alter the course of the liver disease.
The one exception is HEV infection, which, for unknown reasons, runs a more severe course in
pregnant patients, with fatality rates of 10% to 20%.
Viral hepatitis (HAV, HBV, HCV, and even HBV + HDV) is the most common cause of jaundice in pregnancy.
While these women require careful
clinical management, pregnancy does not specifically alter the course of the liver disease.
The
one exception is what?
HEV infection,
which, for unknown reasons, runs a more severe course in
pregnant patients, with fatality rates of 10% to 20%.
A very small subgroup of pregnant women (0.1%) develops hepatic complications directly
attributable to pregnancy: what are these complications?
- preeclampsia and eclampsia,
- acute fatty liver of pregnancy, and
- intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
NOTE: In extreme cases of the first two conditions, the outcome is fatal.
Preeclampsia affects 3% to 5% of pregnancies and is characterized by what?
- maternal hypertension,
- proteinuria,
- peripheral edema,
- coagulation abnormalities, and
- varying degrees of disseminated intravascular coagulation ( Chapter 22 ).
What is eclampsia?
When hyper-reflexia and convulsions occur the
condition is called eclampsia and may be life-threatening.
What is HELLP syndrome?
Alternatively, subclinical hepatic
disease may be the primary manifestation of preeclampsia, as part of a syndrome of _hemolysis,
elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets_, dubbed the HELLP syndrome.
What is the morphology of the affected liver in preeclampsia?
The affected liver in preeclampsia is normal in size, firm, and pale, with small red patches due to hemorrhage.
Occasionally, yellow or white patches of ischemic infarction
can be seen.
What is the microscopic morphology of the affected liver in preeclampsia?
Microscopically,
the periportal sinusoids contain fibrin deposits with
hemorrhage into the space of Disse, leading to periportal hepatocellular coagulative
necrosis.
Blood under pressure may coalesce and expand to form a hepatic hematoma;
dissection of blood under Glisson’s capsule may lead to catastrophic hepatic rupture ( Fig. 18-42 ).
Patients with hepatic involvement in preeclampsia may show modest to severe elevation of what lab findings?
serum aminotransferases and mild elevation of serum bilirubin.
Hepatic
dysfunction sufficient to cause a coagulopathy signifies far-advanced and potentially lethal disease.
What is the definitive treatment for preeclampsia?
. Definitive treatment in severe cases requires termination of the pregnancy.
In mild cases patients may be managed conservatively.
Women who survive mild or severe
preeclampsia recover without sequelae.
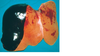
FIGURE 18-42 Eclampsia. Subcapsular hematoma dissecting under Glisson’s capsule in a
fatal case of eclampsia.
What is AFLP?
ACUTE FATTY LIVER OF PREGNANCY (AFLP)
AFLP presents with a spectrum ranging from modest or even subclinical hepatic dysfunction
(evidenced by elevated serum aminotransferase levels) to hepatic failure, coma, and death
. It is a rare disease affecting 1 in 13,000 deliveries. Affected women present in the latter half of
pregnancy, usually in thethird trimester.
Symptoms are directly attributable to incipient hepatic
failure, including bleeding, nausea and vomiting, jaundice, and coma. In 20% to 40% of cases
the presenting symptoms may be those of coexistent preeclampsia.
The diagnosis of acute fatty liver of pregnancy rests on biopsy identification of the what?
characteristic microvesicular fatty transformation of hepatocytes.
In severe cases there may
be lobular disarray with hepatocyte dropout, reticulin collapse, and portal tract inflammation,
making distinction from viral hepatitis difficult. Diagnosis depends on
- (1) a high index of suspicion and
- (2) confirmation of microvesicular steatosis using special stains for fat (oil-red-O or Sudan black) on frozen tissue sections; electron microscopy may also be used to
demonstrate the steatosis.
What is the clinical course of AFLP?
While this condition most commonly runs a mild course, women with AFLP can progress within
days to hepatic failure and death.

