chapter 1 Flashcards
(80 cards)
what is polarity?
- describes the distribution of charge within a molecule as mediated by electrons
what are nonpolar molecules?
- in nonpolar molecules, electrons are distributed fairly evenly, although transient and induced dipoles may be present
what are polar molecules?
- In polar molecules, one or more electronegative atoms attract electrons creating areas of higher electron density or low electron density
what are charged molecules?
- charged molecules have one or more full positive or negative charges
what is the concept “functional group”?
- a useful way to explain the reactivity and chemical/physical properties of classes of molecules
- it’s a specific group of atoms that contribute in a predictable way to the behaviour of a molecule
functional groups on a spectrum of polarity from least to most polar:
- hydrocarbons
- aldehydes and ketones
- amines (primary and secondary)
- alcohols
- carboxylic acids
- charged molecules
What happens if a molecules has more than one functional group?
- look at if the non polar aspects of the molecule outweigh the polar aspects
- ex. steroids
what are amphipathic molecules?
- they exhibit significant polar and nonpolar properties localized to different parts of the molecules
- ex. fatty acids which have a polar head and a nonpolar tail
what determining whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar, what should be taken into account?
- its molecular geometry
- look for dipoles cancelling each other out!
polarity is also often discussed in terms of what?
- solubility
- like dissolves like
how can polar molecules be described?
- water-soluble
- hydrophilic
- lipophobic
how can non-polar molecules be described?
- non-water soluble
- hydrophobic
- lipophilic
what are proteins?
- the building blocks of life which are composed of amino acids
what is the structure of an amino acid?
the central carbon has 4 substituents
- has an amine functional group
- a carboxylic acid functional group
- an H group
- an R group unique to each amino acid (side chain)
structure and description of glycine?
- non polar
- achiral
- Gly
- G

structure and description of alanine
- nonpolar
- Ala
- A

structure and description of Valine?
- Val
- V
- nonpolar
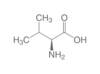
structure and description of isoleucine?
- Ile
- I
- nonpolar

structure and description of methionine?
- Met
- M
- nonpolar

structure and description of proline?
- Pro
- P
- “proline kink”

structure and description of phenylalanine?
- Phe
- F
- nonpolar

structure and description of tyrosine?
- Tyr
- Y
- Pka of 10
- nonpolar
- aromatic

structure and description of tryptophan?
- Trp
- W
- nonpolar
- aromatic

structure and description of serine
- Ser
- S
- polar uncharged


























