Ch7-Analyzing Ethernet LAN Switching Flashcards
(26 cards)
An Ethernet frame sent to destination address FFFF.FFFF.FFFF, meaning that the frame should be sent to all hosts on that LAN
broadcast frame
An Ethernet frame whose destination MAC address is listed in a switch’s MAC address-table, so the switch will forward the frame out the one port associated with that entry in the MAC address-table
known unicast frame
A protocol that allows a switch to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by detecting loops and removing them by blocking selected switch interfaces
Spanning Tree Protocol
An Ethernet frame whose destination MAC address is not listed in the switch’s MAC address-table, so the switch must flood the frame
unknown unicast frame
A table of forwarding information held by a Layer 2 switch, built dynamically by listening to incoming frames and used by the switch to match frames to make forwarding decisions
MAC address table
To send a frame received in one interface out another interface, toward its ultimate destination
forward/forwarding
The result of the LAN switching forwarding process for broadcasts and unknown unicast frames. These frames are forwarded all interfaces, except for the interface on which the were received
flooding
Command reference: Shows all MAC address table entries of all types
show mac address-table
Command reference: Shows all dynamically learned MAC table entries
show mac address-table dynamic
Command reference: Shows all dynamically learned MAC table entries in particular vlan
show mac address-table dynamic vlan vlan-id
Command reference: Shows the dynamically learned MAC table entries with that particular MAC address
show mac address-table dynamic address mac-address
Command reference: Shows all dynamically learned MAC table entries associated with a particular interface
show mac address-table dynamic interface interface-id
Command reference: Shows the number of entries in the MAC table, and the total number of remaining empty slots in the MAC table
show mac address-table count
Command reference: Shows the global and per-VLAN aging timeout for inactive MAC table entries
show mac address-table aging-time
Command reference: Clears the MAC address table of all dynamic entries
clear mac address-table dynamic
Command reference: Lists one line per interface on the switch, with basic status and operating information for each
show interfaces status
Which command likely produced the following output?

show mac address-table dynamic
Which command likely produced the following output?
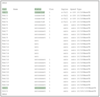
show interfaces status
Which command likely produced the following output:

show interfaces fa0/1 counters
In the figure, the first command lists all dynamicly learned MAC addresses. What two possible commands could have resulted in the bottom output?

show mac address-table dynamic address 0200.1111.1111
show mac address-table dynamic interface fa0/1
What command produced the following output:

show mac address-table aging-time
What command produced the follwing output:

show mac address-table count
What are the three main functions of a LAN switch?
- Forward frames based on destination MAC address
- Learn and fill the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address and port of incoming frames
- Prevent switching loops via STP
Describe the process of forwarding a known unicast frame.
- Examine the destination MAC address
- Compare destination MAC address to MAC address table and match the destination port
- Forward the frame through the matched port
- Filter the frame from all other ports


