Ch.41-Kidneys and Ureters Flashcards
(50 cards)
What are your radiographic findings and ddx?

Discussion question…

Breed over represented in forming polycystic kidneys?
Inherited polycystic kidney disease is seen in
long-haired cats (autosomal dominant), sometimes associated
with hepatic and pancreatic cysts
***In dogs, cairn terriers (recessive
mode of inheritance) and can be identified at a young age.***
CT image findings?

Transverse computed tomography (CT) image of the urethra
and distal ureters in a dog with bilateral ectopic ureters. The two ureters
(white arrows) course dorsal to the urethra. They inserted into the urethra
just caudal to this image plane.
Dosage for contrast for CT:
IV contrast 400 to 800 mg I/kg body weight
What’s yor dx?

Abscess in crania pole of kidney
the cranial pole of the kidney is enlarged and contains a poorly delineated hypoechoic cavity. A focus of hyperintensity w/ reverberation artifact is seen (consistent w/ gas)
What is Pre-ureteral vena cava (or circumcaval ureter)?
a common vascular anomaly in cats (prevalence of 22.4%) where the ureter courses dorsal to the caudal vena cava and displaces the vena cava ventrally. This anomaly has been associated with ureteral strictures in people and may predispose cats
for urinary tract signs.
Indications of renal evaluation via US:
Any signs of renal dysfunciton
**Ultrasound is the method of choice to evaluate renal architecture
and vascularity**
Dx based on this US image?

ureterolith
When do you take rads after contrast administration in excretrory urography?
VD and right lateral radiographs are acquired
immediately after injection and are repeated typically after 5,
20, and 40 minutes or until a diagnosis is reached.
Differential diagnoses for ureteral dilatation include:
obstruction (e.g., calculi, clots, strictures, masses), ectopic ureter, inflammation (e.g., ureteritis, pyelonephritis), atony, and ureteral tears.
Explain what happens wafter giving the contrast in an excretory urography?
- renal areteries become opacified approx. 5-7 seconds post injection
- excretory urogram can be divided in 2 phases:
- nephrogram phase: uniform opacification of the renal parenchyma. begins after ~10 secs post inj and lasts up to 2 min until pyelogram phase starts
- pyelogram phase: contrast is concentrated in the renal tubules
Ddx:

hypercalcemia
FIP
acute tubular necorsis
lepto
pyogranulomatous vasculitis
Perirenal or subcapsular fluid may be the
result of:
acute renal failure, urine leakage, ureteral obstruction,
hemorrhage, abscessation, perirenal pseudocysts, and neoplasia.
Abdominal or pelvic canal trauma may affect the kidneys
and/or ureters. What image modality allows most complete evaluation of these damages?
CT provides the most complete evaluation of suspected renal trauma.CT allows simultaneous assessment of trauma to soft tissue and bones, as well as blood supply of injured
organs
What’s your dx?

Ventrodorsal (VD) oblique radiograph from an excretory
urogram of a dog with bilateral ectopic ureter.
What are your findings?

Dilation of right renal pelvis and ureter
the renal pelvis is distended
but not filled with contrast medium; instead there is a large filling defect. This filling defect extends into a
dilated, tortuous proximal ureter, obstructing it (B, arrow).

Advantages of antegrade US Pyelography? And what is the indication to do this procedure? What are some contraindications?
This procedure can be performed in azotemic patients without
loss of image quality. In addition, each renal pelvis and ureter
can be assessed individually.
The main indication for this procedure is suspected
ureteral obstruction. Renal pelvis diameter should e at least 5mm
Patients w/ coagulopathies
What’s your ultrasonographic findings and most likely dx?
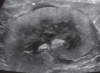
Renal lymphoma tends to occur bilaterally and causes
enlarged, irregularly shaped kidneys with a hyperechoic cortex.
Focal or multifocal nodules and masses have also been
reported.
What’s your ultrasonographic findings and most likely dx?

Ethylene glycol toxicity leads to the most dramatic increase
in cortical and medullary echogenicity with a hypoechoic
rim at the corticomedullary junction and hypoechoic central
medullary regions
Other tumors that
may affect the kidneys are:
histiocytic sarcoma, plasma cell
tumor, metastatic carcinoma, hemangiosarcoma, and lympho-
sarcoma.
How do kidneys look in CT?
soft tissue attenuating, except for a small
amount of fat surrounding the renal pelvis.
What are your US findings:

Pelvis dilation due to pyelonephritis. The renal
medulla is hyperechoic, resulting in poor corticomedullary definition. The
retroperitoneal fat surrounding the kidney is very hyperechoic and inflamed.
Acute pyelonephritis can lead to mild renal enlargement,
whereas renal size is reduced in chronic pyelonephritis.
Peninephric speudocyst has been associated with what disease?
Pseudocyst formation is caused by a transudate and has been
associated with underlying renal parenchymal disease, such as
interstitial nephritis. The affected kidneys are often reduced
in size and have signs of chronic renal disease
US signs of acute renal injury
Ultrasonographic findings associated
with acute kidney injury leading to acute tubular nephrosis
or necrosis, interstitial nephritis or glomerulonephritis include
renal enlargement, subcapsular or perirenal effusion, and
cortical hyperechogenicity.








