Ch. 40- Liver and Spleen Flashcards
Ddx for gallbladder edema:
right sided congestive heart failure
portal hypertension
hypoproteinemia
sepsis
anaphylaxis
What’s your ultrasonographic description and most likely dx?
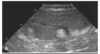
Multiple well defined hyperechoic nodules in the spleen. Myelolipomas
What is your most likely diagnosis

Acute splenic infarction
What’s your dx?

gallbladder edema
What are some ddx in a dog with these findings in US?

Lymphoma, MCT, Histiocytic sarcoma
*** disclaimer- there are more ddx… can you nae more ddx? *****
nodular hyperplasia, hematoma, focal extramedullary hematopoiesis, abscess, and infarction
Causes of hypoechoic liver:
lymphoma, hepatic congestion, leukemia, amyloidosis, cholangiohepatitis, acute hepatitis
Causes of hyperechoic liver:
hepatic lipidosis
vacoular hepatopathies
chronic hepatitis
hepatic cirrhosis
What’s your dx?

Emphysematous splenic torsion
Causes of generalized hepatomegaly:
Hepatic congestions, steroid hepatopathy, hepatic lipidosis,inflammatory and infiltrative disease, primary neoplasia
what part of the spleen is fixed in the left craniodorsal aspect of the stomach?
proximal extremity of the spleen
What is your dx?

Dilation of caudal vena cava and hepatic veins
Radiographic signs of generalized hepatomegaly:
rounding or blunting of the caudoventral liver margins
extension beyond the costal arch
caudal displacement of the gastric axis
Causes for focal hypoechogenicity in the liver:
Cysts, abscesses, primary or metastatic neoplasia, hematomas, granulomas, nodular hyperplasia, and focal extramedullary hematopoiesis
In cats, gallbladder wall thickness should be:
In dogs, gallbladder wall thickness should be:
<1mm or not visualized at all
1-2mm
What’s your dx?

Cystic mucinous hyperplasia
What is your most likely dx?

Metastaic neoplasia due to the target lesion in the spleen
Mineral opacities can occur in the hepatic parenchyma or biliary system. Give possible causes for mineralization of bith liver and biliary system.
liver- dystrophic calcification of hepatic granulomas, abscesses, hematomas, neoplastic masses or areas of necrosis
biliary tree- choleliths, gall bladder carcinoma, cholecystitis or cystic mucinous hyperplasia
What is your dx?

GB mucocele w/ GB wall rupture
(Gallbladder mucocele is an accumulation of nondependent sludge, semisolid mucus, and inspissated bile, creating an intraluminal centralized echogenicity with peripheral striations, creating a stellate appearance)
Most common cause of extrahepatic biliary obstruction in the dog:
Pancreatitis is one of the most common causes of extrahepatic biliary obstruction in the dog, with neoplasia of the liver, bile duct, pancreas, or duodenum also capable of causing obstruction
Thickening of the gallblader wall indicate:
Thickening of the gallbladder wall is a nonspecic sign found with primary gallbladder inflammation or neoplasia, or secondary to systemic diseases that have a secondary effect on the gallblad- der wall.
What’s your dx?
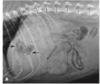
There is an irregular focal radiolucency in the midportion of the liver due to hepatic abscessation secondary to hepatic carcinoma (other ddx include necrosis of the liver, gas producing bacteria)
What is the structure that the white arrow is pointing at? What could this structure represent?

Target lesions. They represent metastatic disease.
What is your dx?

Cholangitis
What’s your dx?
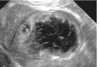
Gallbaldder wall thickening secondary to potential cholycystitis
What’s your dx?

dilation of CBD
What’s your dx?

Cholelith
Causes of diffuse splenomegaly:
Considerations for diffuse splenomegaly are numerous and include inflammation caused by infection with toxoplasmosis, fungal organisms, Mycoplasma haemofelis, ehrlichiosis, hyperplasia (e.g., hemolytic disorders), systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic bacteremic disorders, congestion (e.g., from impaired venous drainage), portal hypertension, splenic torsion/ infarction, anesthetic drugs, and infiltrative disease (e.g., primary (Lymphosarcoma, leukemia, systemic mastocytosis, multiple myeloma, and malignant histiocytosis) and metastatic neoplasia, and extramedullary hematopoi- esis), splenic torsion
True or False. Portal veins are smoothly tapering vessels characterized by bright, echogenic borders.
True
Normal CBD diameter in cats is:
Normal CBD diameter in dogs is:
<4mm
3mm or less
What is the most common primary hepatic tumor in dogs? what could be other examples of primary tumors?
hepatocellular carcinoma
other examples include: cholangiocarcinoma, neuro endocrine tumor, and histiocytic sarcoma
Treu or False. In US the liver is usually hyperechoic to the spleen. Why?
False. Liver is usually hypoechoic to the spleen
Is the liver enlarged? why or why not?

The liver is not enlarged. This is a cat w/ pleural effusion and the thorax is overexpanded which results in caudal displacement of the diaphragm and liver
Is this a normal or abnormal finding?

Normal liver. Normal finding in young dogs and cats
Causes of diffuse splenomegaly:
Extramedullary hematopoiesis, splenic congestion, phenothiazines (phenobarb), diffuse neoplastic infilatration (lymphoma, MCT, histiocytic sarcoma), splenitis ( due to fungal- histoplasmosis in cats)
When is splenomegaly considered in the cat in rads?
Splenomegaly in the cat is considered if the distal extremity is visible on the lateral projection of the abdomen.
What are target lesions?
Focal masses with a hyperechoic center and hypoechoic periphery
***but they have been reported with benign disease processes***
Ddx splenic mass:
Include benign and neoplastic conditions. Primary and metastatic neoplasia, hematoma, nodular hyperplasia, extramedullary hematopoiesis, and abscess are all considerations.
The spleen has no absolute size limits in the dog. The normal feline spleen is less variable in size than the dog, and objective measurements have been determined what?
to measure no more than 0.1 cm in the transverse plane
What’s your dx?

A. hypoattenuating mass in the liver located in the left lateral lobe (most likely primary neoplasia-hepatocellular carcinoma)
B. multi focal hypoattenuating nodules in the liver and gall bladder edema (most likely metastatic dz)
What’s your dx and main ddx? This is an image of the liver.
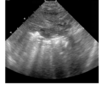
ehogenic shadows and reverberation artifacts in the liver. The cause of these reverberation artifacts is due to gas. Possible ddx: abscessation or necrosis
What’s your dx?
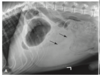
Splenic torsion
** gas can be also noted in splenic torions**
What are some nonpathologic conditions that can result in extension of hepatic margins beyond the costal arch
overexpansion of the thorax or deep inspiration
older dogs and cats can have stretching or elongation
obese patients
some brachycephalic and chondrodystrophic breeds
neonatal patients
What modalities you can use to detect PSS?
US
CT
MRI
Nuc Med
What’s your dx?

Multiple hypoechoic nodules in the liver giving a honeycomb appeatance (hepatocutaneous syndrome)
How to calculate GB volume in cats and dogs:
Height x width x length x 0.52= ___mL
Dogs 1mL/kg
Cats 2.4mL regardless of the weight
How to calculate the proper contraction and function of GB in dogs:
1) 12 hr fast
2) calculate GB volume
3) feed that dig
4) wait 2 hrs
5) calculate GB volume
6) find the difference between the 2 values. This should be ~25% or greater.


