Cerebral cortex (8.3) Flashcards
Identify and describe the lobes of the brain

Describe the cerebral cortex in relation to the rest of the forebrain, brainstem and cerebellum
Cerebral cortex: The outer layer of the cerebrum. Composed of folded gray matter (neuronal bodies). Plays an important role in consciousness. Arranged into 3 layers, each with a differing number of cellular layers
- Neocortex: 6 layers
- Only has 3 layers in the cerebellum
- Archicortex 4 layers
- Paleocortex: 3 layers
Describe the neurons in the CNS and the consequences of damage
Key groups
Substantia nigra:
- Midbrain
- Dopaminergic neurones
- Damage → Parkinson’s
Raphe nucleus magnus
- Medulla
- Serotonergic neurones
- Damage/loss → depression
Locus coeruleus
- Pons
- Noradrenergic neurones
- Damage/loss → depression
Cholinergic
- Damage → Alzheimer’s
Glutaminergic
- Over stimulation → epilepsy, excitotoxic shock
GABAergic
State the difference between grey and white matter
Gray matter: Located around the ‘exterior’ aspect of the cerebrum. Contains the cell bodies of neurons.
White matter: Located ‘centrally’. Contains the axons/processes of neurons.
Explain the core functions of areas around the cortex

Describe the homonculus for the motor and sensory cortices

Explain how the cortices provide contralateral supply
Decussation of neuronal fibres from the cerebral hemispheres means that each hemisphere provides motor and sensory innervation to the contralateral musculature
State the functional dominance of the left and right hemispheres
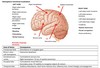
State the effects of lesions to the cortex:
ACA, MCA, PCA, temporal, parietal, frontal, FEF, Broca’s, Wernicke’s
SEE PREVIOUS
For arterial lesions/occlusions refer to homunculus


