Cell Adaptaton Flashcards
(27 cards)
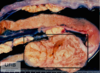
This condition is caused by poor nutrition and is characterized by dilated lymphatics with a jelly-like substance on the outer surface of the heart.
What is the name of this type of atrophy?

Serous atrophy of fat
How is brain atrophy characterized?
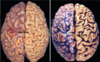
Gyri are narrowed
Sulci are widened
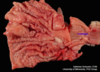
Serous Atrophy of Fat can occur on the heart and the in the bone marrow. T / F
TRUE!!
What is the name of this type of Atrophy?

Serous Atrophy of Fat
Jelly-like material occurs in the middle (arrow) where bone marrow should be.

What type of atrophy is this?
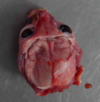
Severe Compression Atrophy (due to hydrocephalus), cat
Hydrocephalus - CSF is not being removed fast enough, increasing intracellular pressure

What type of Hypertrophy is this?
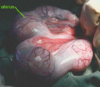
Physiologic Hypertrophy
Examples:
- Pregnant Uterus
- Weightlifter
When a weightlifter bulks up in size this is an example of what?
Physiologic Hypertrophy
This condition is:
A. Left concentric hypertrophy, Right eccentric hypertrophy
B. Right concentric hypertrophy, Left eccentric hypertrophy
C. Concentric cardiac hypertrophy, bilateral
D. Eccentric cardiac hypertrophy, bilateral

Eccentric cardiac hypertrophy, bilateral
This condition is:
A. Left concentric hypertrophy, Right eccentric hypertrophy
B. Right concentric hypertrophy, Left eccentric hypertrophy
C. Concentric cardiac hypertrophy, bilateral
D. Eccentric cardiac hypertrophy, bilateral

Left concentric cardiac hypertrophy with right eccentric hypertrophy
This disease is:
- common in Main Coon Cats
- caused by Mutation in the MYBPC3 gene
- is an inherited autosomal dominant mutation
What is the name of this condition?

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- a type of pathological hypertrophy
What does Atrophy, Hyperplasia and Hypertrophy have in common?
- all are adaptive changes
- they can occur physiologically or pathologically
Hyperplasia is:
A. Increase in cell number
B. Capable of cell replication
C. Physiological (Hormonal, Compensatory)
D. Pathological (Epidermal thickening, Respiratory mucosa)
E. B and C only
F. All of the above
All of the above
Give two examples of Physiological Hyperplasia.
- Hormonal - breast cell numbers increase during pregnancy
- Compensatory - Hepatectomy, so other liver lobe must increase in size to compensate
Give two examples of Pathological Hyperplasia.
- Repeated irritation causing -> epidermal thickening
- Viral infections - more respiratory mucosa
“Most commonly caused by excessive hormonal or growth factor stimulation”
Is this Hyperplasia pathological or physiological?
Pathological hyperplasia
This is an example of what type of Hyperplasia?

Pathological Hyperplasia

Epidermal Thickening: Deep thick layers invaginating deep down.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in cats is an example of:
A. Hormonal (physiological) hyperplasia
B. Epidermal (pathological) hyperplasia
C. Respiratory (pathological) hyperplasia
D. Compensatory (physiological) hyperplasia
E. B and C
Epidermal pathological hyperplasia
- cats usually get SCC in the pinna of the ear
- hyperplasia leads to dysplasia, carcinoma in situ and invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
What is the MDx of this condition?

MDx: Fibrous hyperplasia
(formerly part of fibrous or fibramatous epulis, gingival hypertrophy)

What is metaplasia?
A change in phenotype of a differentiated cell;
One cell type is changed to another cell type.
_______________is the response to chronic irritation.
Metaplasia
Metaplasia results in:
- increase/decreased function
- increased / decreased risk of malignant transformation
- DECREASED function
- INCREASED risk for malignant transformations
Give 4 examples of Metaplasia
- Chronic irritation in the lungs (smokers)
- Vitamin A Deficiency
- Estrogen toxicity
- Intra mammary tumors
Is this an example of atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia or dysplasia?
Dysplasia: Squamous cell carcinoma in situ
“Carcinoma in situ” because is a neoplastic process so the word dysplasia is replaced with carcinoma in situ.

Is this an example of atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia or dystrophy?

Gastric Hypertrophy
MDx: Stomach, diffused marked chronic gastric hypertrophy
EDx: Cryptosporidium serpentis
(increase in size of the mucosa)