Case Studies - Exam I Flashcards
Horse:
Is this a post-mortem change or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx and Etiology (Etx)?

MDx: Post-mortem Artifactual Nasal Froth
Etx: Common artifact of dying
Lesion or Disease name: Nasal Froth
*Side note: this occurs when there is pulmonary edema, which then leaks out after death
Cat:
Is this a post-mortem change or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Post-mortem change
MDx: Pleural cavity, euthanasia solution artifact
*side note: dark brown surfaces with odor of alcohol*
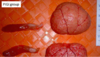
Cow:
Is this a post-mortem change or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx and EDx?
Post-mortem change
MDx: Liver, artifact reverse flow of brain
EDx: Increased air pressure result during slaughter
Description: Pale white soft tissue in the hepatic vein
Caribou calf:
Is this a post-mortem change or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Post-mortem change
MDx: Carcass, post-mortem caused carcass damage
*Remarks: failure to see blood around the carcass damage suggests that this finding is only an artifact (animal predation) caused after death*
Pig:
Is the black, outlines a post-mortem change or an actual lesion?
What is the name of the black outlines and what causes it?
What is the *MDx?

Pseudomelanosis (black outlines) is a Postmortem change
MDx: Liver, bile ducts subacute purulent (suppurative) choangitis
Pseudomelanosis (black outlines): is considered a postmortem change due to the bacterial action on the blood producing disulfides
*at this point we are only supposed to know pseudomelanosis as we have not been taught about choangitis
What is pseudomelanosis?
Pseudomelanosis (black outlines): is considered a postmortem change due to the bacterial action on the blood producing disulfides
Horse:
Is the grey appearing mucosa a post-mortem change or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Grey mucosa: a post-mortem artifactual change
MDx: Colon, acute necrotizing colitis
*the grey appearing mucosa surrounding bowel is primarily autolytic change and artifactual*
Normal mucosa should be pink or pale pink
Dog:
Is this a post-mortem artifact or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Post-mortem artifact (Livor mortis / hypostatic congestion)
MDx: Brain, meninges, unilateral darkened (Hypostatic congestion)
*the R. side of the brain is darker red than the L. side; animal was lying on it’s right side at the time of death resulting in Hypostatic Congestion*
Pig:
Is this a post-mortem artifact or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?
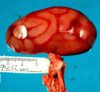
Post-mortem artifact / change
MDx: Kidney, terminal congestion with intestinal loop pressure artifacts of no blood.
*terminal congestion = hypostatic congestion/livor mortis*
Cow:
Are the brown/red dots a post-mortem artifact or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Post-mortem artifact
MDx: Liver, normal (hemorrhage) artifact during slaughtering process
Dog:
Are the large black areas post-mortem artifact or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Post-mortem artifact
MDx: Spleen, multifocal unequal explusion of blood
Result of some scattered areas of smooth muscle contraction preventing blood escape at death or soon after.
Calf:
Is the eye discoloration a post-mortem artifact or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?

Post-mortem artifact
MDx: Eye, corneal clouding (opacity)
Cow:
Is this a post-mortem artifact or an actual lesion?
What is the MDx?
What is the etiology (Etx)?

An actual lesion (see EDx)
MDx: Larynx, trachea: severe, diffuse, fibrinonecrotic, laryngitis and tracheitis.
Etx: Bovine Herpesvirus-1
*on Destany’s exam
Pig:
What is the MDx?
What are 3 possible causes (Etx)?

MDx: Abdominal serosal surfaces: severe, acute, diffuse, fibrinous peritonitis.
Haemophilus parasuis:
Etx1: Streptococcus suis
Etx2: Mycoplasma hyorhinis
Etx3: Escherichia coli
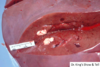
Feline Tongue:
What is the pathogenesis of these lesions?

Pathogenesis:
Renal insufficiency -> elevated levels of circulating BUN -> breakdown by oral bacteria produces ammonia -> caustic burns -> ulcerative glossitis
*side note: Glossitis = inflammation of the tongue*
*on two of Destany’s exams