CBL4 Bronchiectasis and Pneumonia Flashcards
What’s bronchiectasis?
(in terms of simple pathology)
Bronchiectasis describes a permanent dilatation of the airways secondary to chronic infection or inflammation.

Causes of bronchiectasis
Causes
- post-infective: tuberculosis, measles, pertussis, pneumonia
- cystic fibrosis
- bronchial obstruction e.g. lung cancer/foreign body
- immune deficiency: selective IgA, hypogammaglobulinaemia
- allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
- ciliary dyskinetic syndromes: Kartagener’s syndrome, Young’s syndrome
- yellow nail syndrome
Physical signs of bronchiectasis
- Clubbing
- Coarse inspiratory creps
- Wheeze
- Purulent sputum
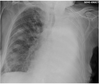
What characteristic features can be seen on that X-ray?
What’s the diagnosis?

- Chest x-ray showing tramlines, most prominent in the left lower zone
- Diagnosis: bronchiectasis
- What can be seen on that X ray? (characteristic feature) (2)
- What’s the diagnosis?

- CT chest showing widespread tram-track and signet ring signs
- diagnosis: bronchiectasis

Main organisms causing infections in bronchiectasis
- H. influenza
- Pneumococcus
- S.aureus
- Pseudomonas
4 main categories of causes of bronchiectasis
- Post infective
- Cystic fibrosis
- Ciliary dyskinetic syndrome
- . Bronchial obstruction - lung cancer
Investigations for Bronchiectasis
- Sputum
- Blood - test for IgG, Alpha 1 anti trypsin
- Chest X ray - tramlines and rings
- Spirometry - obstructive
- CT - dilated and thickened airways
- Cystic fibrosis sweat test
Differential diagnosis for bronchiectasis

Normal antibiotics used to treat bronchiectasis exacerbation?
- Amoxicillin / Clarithromycin
- Tazocin if IV
Symptoms of bronchiectasis

Characteristics of the cough in bronchiectasis
- productive
- worse in the morning
- large volume
- daily purulent sputum
Investigations in bronchiectasis (just in general)
- spirometry
- CXR
- CT
- sputum culture
What pattern of spirometry may be seen in bronchiectasis?
Obstructive or normal
Characteristic features of CXR in bronchiectasis
- May be normal
- Ring opacities, tram-tracks
- Fluid-filled cysts or bronchocoeles
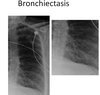
Characteristic features of CT in bronchiectasis
- Signet ring sign and tram-tracks
- Lack of tapering of airways - thickness is NOT reduced towards the end
- Mucus impaction
- Mosaicism (vessels of different size in different regions of the lungs - smaller where less perfused)

Investigations for Bronchiectasis
Sputum MCS
Blood: Se Ig, Aspergillus precipitins, RF, α1-AT level
Test Ig response to pneumococcal vaccine
CXR: thickened bronchial walls (tramlines and rings)
Spirometry: obstructive pattern
HRCT chest - Dilated and thickened airways
- Saccular dilatations in clusters c¯ pools of mucus
Bronchoscopy + mucosal biopsy
Focal obstruction PCD
CF sweat test (pilocarpine iontopheresis)
Management of bronchiectasis
- physiotherapy (e.g. inspiratory muscle training) - has a good evidence base for patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis
- postural drainage (airway clearance)
- antibiotics for exacerbations + long-term rotating antibiotics in severe cases
- bronchodilators in selected cases
- immunisations (influenza and bronchodilators)
- surgery in selected cases (e.g. Localised disease)
3 major symptoms of bronchiectasis
- Persistent cough and purulent sputum
- Haemoptysis
- Fever, weight loss and malaise
Most common organisms isolated from patients with bronchiectasis (4)
Most common organisms isolated from patients with bronchiectasis:
- Haemophilus influenzae (most common)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Klebsiella spp.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
M
Management of infective exacerbations in bronchiectasis (what to do in general)
- Review previous sputum culture results & most recent course of antibiotics given
- Send more sputum for culture
- Choose antibiotic (in line with local guidance):
–amoxicillin/clarithromycin/doxycycline oral
–ciprofloxacin if Pseudomonas aeruginosa
–Tazocin/3rd generation cephalosporin IV
*Total course 10-14 days
*May need to consider outpatient IV antibiotics
•Chest physiotherapy
Antibiotics used in infective exacerbations of bronchiectasis
- what oral antibiotics
- what for Pseudomona aeurginosa
- what IV antibiotic
- how long for
* Choose antibiotic (in line with local guidance):
–amoxicillin/clarithromycin/doxycycline oral
–ciprofloxacin if Pseudomonas aeruginosa
–Tazocin/3rd generation cephalosporin IV
- Total course 10-14 days
- May need to consider outpatient IV antibiotics
How to treat pseudomonas aureginosa exacerbation of bronchiectasis?
Ciprofloxacin