Cartilage and Bone Flashcards
(54 cards)
Types of cartilage (specialized CT)
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
Cartilage
- contains collagen II
- contains sulfated proteoglygans (e.g. aggrecan) plus other ECM proteins dependent on cartilage type
- net negative charge (basophilic)
- avascular & aneural
- chondrocytes in isogenous groups
Types of bone tissue (specialized CT)
- Woven
- Lamellar
- Compact (includes Haversian bone)
- Spongy (cancellous, trabecular)
all contain calcium hydroxyapatite

Hyaline Cartilage
translucent (think: Glass)
very hydrated; resists compression
smooth
located in all articular joint surfaces
- isogenous groups (back-to-back D’s: D)
- territorial matrix - TM (very basophilic)
- homogeneous interterritorial matrix - ITM (less basophilic)
- abundant sulfated PGs (e.g. aggrecan, thus very hydrated)
- cells retracted from lacunae (L. “lake” or “lagoon”)
- perichondrium at edges (but NOT at articular surfaces)
- grows by both interstitial & appositional deposition

Elastic Cartilage
similar to hyaline but also contains elastic fibers
found in external ear, eustachian tube, epiglottis
- isogenous groups (back-to-back D’s:D)
- territorial matrix
- elastic fibers present surrounding cells and in interterritorial matrix
- perichondrium
- interstitial/appositional growth

Fibrocartilage
hydrated (resists compression) but also contains collagen I so also high in tensile strength
found in intervertebral discs, temporomandibular joints, public symphysis
- isogenous groups (back-to-back D’s:D)
- territorial matrix not obvious
- wavy collagen fibers (type I) present, thus eosinophilic
- NO perichondrium
- has fibroblasts
- interstitial growth

Interstitial growth
pushes to side
Appositional growth
on top of eachother
Location of hyaline cartilage
articular surfaces
Elastic fibers
look like wires
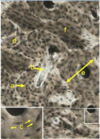
ID the type of tissue and the type of growth

Hyaline Cartilage
Appositional growth (left) and Interstitial growth (right)
Chondrocytes
Cartilage cells
Osteoarthritis
progressive, wear & tear joint disease of unknown cause

Rheumatoid arthritis
Autoimmune, destruction of cartilage

Woven Bone
- immature bone
- disorderly arrangement of collagen

Lamellar Bone
Compact
- Haversian systems
- concentric lamellae
- osteocytes interconnected by processes within canaliculi
- central Haversian canal
- interstitial lamellae
- periosteum & endosteum
Spongy (aka cancellous, trabecular)
- lamellae
- osteocytes interconnected by processes within canaliculi
- endosteum

Histological preparation of bone tissues

ID Type

Woven bone (immature bone)
ID Type of Bone and Labeled sections

Compact Bone
Volkman’s Canal (A) and Interstitial Lamallae (IL)
Interstitial Lamallae
space between osteons, remnants of osteons that were partially resorbed during the process of bone remodeling

Canaliculi
microscopic canals between the lacunae of ossified bone
Interconnect osteocytes in life

Lacunae
where osteocytes lived
a small space containing an osteocyte in bone or chondrocyte in cartilage

Periosteum and Endosteum
endosteum (plural endostea) is a thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the medullary cavity of long bones
periosteum is the membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones,[1]except at the joints of long bones

Spongy (cancellous) bone
contains bone lamallae but not haversian systems