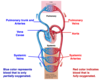
Cardiovascular System Flashcards
What is Hydrostatic Pressure?
The force that is exerted by the blood upon the capillary walls
The hydrostatic pressure changed as you go through the kidneys (decreases as you go)
What is the Frank-Starling Mechanism?
Causes the ventricles to contract with greater force when more blood is present (due to more tension)
What links Mean Arterial Pressure with Peripheral resistance?
MAP = Q x Total PR
At rest, where does most of the blood flow to?
The abdominal organs and kidneys

Explain what Korotkoff sounds are
Systolic - The artery is starting to open, so muffled sounds can start to be heard
Diastolic - The artery is practically open, so all sounds stop

What is the difference between Diastole and Systole?
Diastole - Ventricular relaxation, and blood filling
Systole - Ventricular contraction, and blood ejection
Describe the mechanism that is responsible for the triggering of the SA node
Na+ ions leak through F-type (funny) channels, whilst Ca2+ move in through T-type channels –> causing slow depolarization
Rapid depolarization occurs due to the openining of VG Ca2+ L-type channels
The reopening of K+ channels and the closing of Ca2+ channels cause repolarization

How do you calculate the mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
Diastolic pressure + 1/3 (Pulse pressure)
Pulse Pressure = Difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
At what distance does diffusion become very slow?
1mm
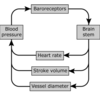
Explain the role of baroreceptors in the maintainance of blood pressure
Located in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses
They fire impulses proportionally to the blood pressure
The signals go to the medulla oblongata, which causes a change in HR/SV/Vessel Diameter via a negative feedback loop
What type of cells does the lymph fluid contain?
Lymphocytes
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
What factor has the greatest effect on blood flow and blood pressure?
The radius of the blood vessel
As its increased by the power of 4

Describe the permeabilities of cellular membranes
Permeable to water
Impermeable to solutes/ions
Therefore Osmosis determins the distribution of water between compartments in the body
Explain the differences in the structure of the arteries, arterioles, veins and capillaries
Arteries - Thick layer of smooth muscle and connective tissue
A large lumen
Arterioles - Contain a thin muscular wall, with smooth muscle that can contract to change the lumen size
A small lumen
Veins - Contain thin walls, and a large lumen
Contain VALVES
Capillaries - Has a single layer of endothelial cells to allow easy exchange of molecules (but not proteins)

How is the SA node innervated?
Parasympathetic = Vagus Nerve
Releases ACh, causing hyperpolarization (decreasing polarization) –> so reducing HR
Sympathetic
Releases Noradrenaline, causing an increase in depolarization –> increasing HR
Both of these systems are active at all times, just in different amounts
Describe the mechanism of contraction of the ventricular cardiomyocytes
Rapid Depolarisation - Rapid opening of VG Na+ channels
Prolonged Depolarization - This causes consistant contraction, and this is caused by the slow (but prolonged) opening of VG Ca2+ channels, and the closure of K+ channels
Repolarization - Opening of K+ channels
Describe the intrinsic (local) regulation of blood flow
Active Hyperemia - An increase in metabolism in the organ causes a decrease in [O2] an increase in [metabolites]
This causes vasodialation –> allowing more blood to go the organ
Flow Autoregulation - When there is a decrease in arterial pressure, there is a decrease in [O2]
Causing vasodialation –> allowing more blood to return to the organ
How does the skeletal muscle pump work in the body?
Contraction of the muscle causes blood to move through open valves in the veins –> and back to the heart

What are short/long term fixes to a change in blood volume?
Short term - Baroceptors firing
Long term - Kidneys (Renin-Agniotensin System)
What are the meanings of the points in an ECG?
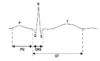
P = Atrial Depolarization
QRS = Ventricular Depolarisation
T = Ventricular Repolarization
PQ = Atrial Contraction
QT = Ventricular Contraction