Cardiovascular Pharmacology Flashcards
Treatment of Primary (Essential) Hypertension by drug type
thiazide diuretics
ACE inhibitors
angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel blockers
Treatment of HTN in Heart Failure by drug type
diuretics
ACE inhibitors/ARBs
beta blockers (for compensated HF)–must use cautiously with decompensated HF and are contraindicated in cardiogenic shock
aldosterone antagonists
Treatment of HTN with diabetes mellitus by drug type
ACE inhibitors/ARBs
Ca2+ channel blockers
thiazide diuretics
beta blockers
treatment of HTN in pregnancy by drug type
hydralazine
labetalol
methyldopa
nifedipine
why are ACE I inhibitors used for HTN with diabetes mellitus?
they are protective against diabetic neuropathy
name the Calcium channel blockers
amlodipine
clevidipine
nicardipine
nifedipine
nimodipine
verapamil
diltiazem
Calcium channel blockers–mechanism
block voltage dependent L type calcium channels of cardiac and smooth muscle–>reduce muscle contractility
which calcium channel blockers act more on vascular smooth muscle?
amlodipine = nifedipine > diltiazem > verapamil
which calcium channel blockers act more on the heart?
verapamil > diltizem > amlodipine = nifedipine
Calcium channel blockers Dihydropyridines (except nimodipine)–clinical use
HTN
angina (including Prinzmetal)
Raynaud phenomenon
Calcium channel blockers Nimodipine–clinical use
subarachnoid hemorrhage–prevents cerebral vasospasm
Calcium channel blockers Clevidipine–clinical use
hypertensive urgency or emergency
Calcium channel blockers Non-dihydropyridines–clinical use
HTN
angina
atrial fibrillation/flutter
Calcium channel blockers non dihydropyridine–toxicity
cardiac depression
AV block
hyperprolactinemia
constipation
Calcium channel blockers dihydropyridine–toxicity
peripheral edema
flushing
dizziness
gingival hyperplasia
Hydralazine–mechanism
increase cGMP–smooth muscle relaxation
vasodilates arterioles more than veins, so afterload reduces
hydralazine–clinical use
severe HTN (particularly acute)
HF (with organic nitrate)
what is the first line of therapy for HTN in pregnant women?
hydralazine with methyldopa
what is hydralazine often coadministered with?
why?
beta blocker
to prevent reflex tachycardia
hydralazine–toxicity
compensatory tachycardia–so contraindicated in angina/CAD
fluid retention
headache
angina
Lupus like syndrome
drugs used for treatment of hypertensive emergency
clevidipine
fenoldopam
labetalol
nicardipine
nitroprusside
Nitroprusside–clinical use
hypertensive emergency
nitroprusside–mechanism
short acting
increases cGMP via direct release of NO
nitroprusside–toxicity
releases cyanide, so can lead to cyanide toxicity
fenoldopam–use
hypertensive emergency
fenoldopam–mechanism
dopamine D1 receptor agonist–coronary, peripheral, renal, and splanchnic vasodilation
decreases BP, inc natriuresis
fenoldopam–toxicity
HTN
tachycardia
name the nitrate drugs
nitroglycerin
isosorbide dinitrate
isosorbide mononitrate
nitrates–mechanism
vasodilate by increasing NO in vascular smooth muscle –> inc in cGMP and smooth muscle relaxation
dilate veins >> arteries, so dec preload
nitrates–use
angina
acute coronary syndrome
pulmonary edema
nitrates–toxicity
reflex tachycardia (treat with beta blockers)
HTN
flushing headache
“Monday disease” in industrial exposure–development of tolerance for vasodilating action during the work week and loss of tolerance over the weekend –> results in tahcycardia, dizziness, headache upon reexposure
antianginal therapy–use
reduce myocardial O2 consumption by decreasing 1 or more of the determinants of myocardial O2 consumption; end diastolic volume, BP, HR, contractility

ranolazine–mechanism
inhibits the late phase of sodium current thereby reducing diastolic wall tension and oxygen consumption
does not affect heart rate or contractility
ranolazine–use
angina refractory to other medical therapies
ranolazine–toxicity
constipation
dizziness
headache
nausea
QT prolongation
name lipid lowering agents
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
bile acid resins
ezetimibe
fibrates
niacin (B3)
what type of Lipid lowering agent decreases LDL the most?
HMG CoA reductase inhibitor
what type of lipid lowering agent increases HDL the most?
niacin (B3)
what type of lipid lowering agent decreases triglycerides the most?
fibrates
what type of lipid lowering agent has NO effect on HDL and triglycerides?
ezetimibe
what type of lipid lowering agent has the smallest effect on lowering LDL?
fibrates
what type of lipid lowering agent only slightly elevates triglycerides?
bile acid resins
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors–mechanism
inhibit conversion of HMG CoA to mevalonate (a cholesterol precursor)
dec mortality in CAD patients
name 5 HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
(-vastatins)
atorvastatin
lovastatin
pravastatin
simvastatin
rosuvastatin
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors–toxicity
hepatotoxicity (inc LFTs)
myopathy (especially when used with fibrates or niacin)
niacin–mechanism
inhibits lipolysis (hormone sensitive lipase) in adipose tissue
reduces hepatic VLDL synthesis
niacin–toxicity
red, flushed fase, which is dec by NSAIDS or long term use
hyperglycemia
hyperuricemia
name 3 bile acid resins
cholestyramine
colestipol
colesevelam
bile acid resins–use
prevent intestinal reabsorption of bile acids
liver must use cholesterol to make more
bile acid resins–toxicity
GI upset
decrease absorption of other drugs and fat soluble vitamins
ezetimibe–mechanism
prevent cholesterol absorption at small intestine brush borders
ezetimibe–toxicity
rare inc LFTs; diarrhea
name fibrate drugs
gemfibrozil
bezafibrate
fenofibrate
fibrates–mechanism
upregulate LDL –> inc triglyceride clearance
activates PPAR alpha to induce HDL synthesis
fibrates–toxicity
myopathy–inc risk with statins
cholesterol gallstones
name a cardiac glycoside
digoxin
cardiac glycosides–mechanism
direct inhibition of Na/K ATPase –> indirect inhibition of Na/Ca exchanger
increase concentration of Ca –> positive intropy
stimulates vagus nerve –> dec HR
cardiac glycosides–use
HF (inc contractility)
atrial fibrillation (dec conduction at AV node and depression of SA node)
cardiac glycosides–toxicity
cholinergic–nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, blurry yellow vision (think van Gogh), arrhythmia, AV block
can lead to hyperkalemia, which indicates poor prognosis
factors that predispose to toxicity with cardiac glycosides
renal failure–dec excretion
hypokalemia–permissive for digoxin binding to K+ binding site on Na/K ATPase
drugs that replace digxin from tissue binding sites
decreased clearance (eg. verapamil, amiodarine, quinidine)
cardiac glycosides–antidote
slowly normalize K+
cardiac pacer
anti digoxin Fab fragments
Mg2+
what are class I antiarrhythmics, and how do they work?
sodium channel blockers
slow or block (dec) conduction especially in depolarized cells
dec slope of phase 0 depolarization
are state dependent (selectively depress tissue that is frequently depolarized, ie. tachycardia)
what causes toxicity in all class I antiarrhythmics?
hyperkalemia
what are the class IA antiarrhythmic drugs?
Quinifine, Procainamide, Disopyramide
“The Queen Proclaims Diso’s pyramid.”
class IA antiarrhythmics–mechanism
inc AP duration
inc effective refractory period (ERP) in ventricular action potential
inc QT interval

class IA antiarrhythmics–use
both atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, especially re-entrant and ectopic SVT and VT
class IA antiarrhythmics–toxicity
cinchonism–headache, tinnitus with quinidine
reversible SLE like syndrome (procainamide)
heart failure (dispyramide)
thrombocytopenia
torsades de pointes due to inc QT interval
what are the class IB antiarrhythmic drugs?
Lidocaine
MexileTine
“I‘d Buy Liddy’s Mexican Tacos”
class IB antiarrhythmics–mechanism
dec AP duration
preferentially affect ischemic or depolarized Purkinje and ventricular tissue
Phenytoin can also fall into the IB category
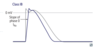
class IB antiarrhythmics–use
acute ventricular arrhythmias (especially post MI)
digitalis-induced arrhythmias
“IB is Best post MI”
class IB antiarrhythmics–toxicity
CNS stimulation/depression
cardiovascular depression
what is the best antiarrhythmic drug to use for a post MI patient?
class IB
what are the class IC antiarrhythmic drugs?
Flecainide
Propafenone
“Can I have Fries, Please?”
class IC antiarrhythmics–mechanism
significantly prolongs ERP in AV node and accessory bypass tracts
no effect on ERP in purkinje and ventricular tissue
minimal effect on AP duration
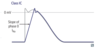
class IC antiarrhythmics–toxicity
proarrhythmics, especially post-MI (contraindicated)
IC is Contraindicated in structural and ischemic heart disease
which class IA antiarrhythmic drug may cause digoxin toxicity?
Quinidine–decreases digoxin clearance and displaces digoxin from tissue binding sites
class IC antiarrhythmics–use
SVTs, including atrial fibrillation
only as a last resort in refractory VT
do not affect AP duration
when are class IC antiarrhythmics contraindicated?
structural heart diseases and post MI
what are class II antiarrhythmics?
name 5
beta blockers
metoprolol
propranolol
esmolol
atenolol
timolol
class II antiarrhythmics–mechanism
decrease SA and AV nodal activity by decreasing cAMP, dec Ca currents
suppress abnormal pacemakers by dec slope of phase 4
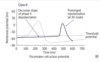
what node is most sensitive to class II antiarrhythmics? and what is the effect of class II antiarrhythmics on the node?
AV node
inc PR interval
which class II antiarrhythmic is most short acting?
esmolol
class II antiarrhythmics–use
SVT
ventricular rate control for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter
class II antiarrhythmics–toxicity
impotence
exacerbation of COPD and asthma
cardiovascular effects (bradycardia, AV block, HF)
CNS effects (sedation, sleep alterations)
may mask signs of hypoglycemia
beta blockers (except non selective alpha and beta antagonists carvedilol and labetalol) cause unopposed alpha 1 agonism if given alone for pheochromocytoma or cocaine toxicity
metoprolol toxicity and how to treat
(classII antiarrhythmic)
can cause dyslipidemia
treat with glucagon
propranolol toxicity
(class II antiarrhythmic)
can exacerbate vasospasm in Prinzmetal angina
how to treat beta blocker overdose
saline
atropine
glucagon
what are class III antiarrhythmics and name 4
potassium channel blockers
Amiodarone
Ibutilide
Dofetilide
Sotalol
“AIDS”
class III antiarrhythmics–mechanism
inc AP duration
inc ERP
inc QT interval

class III antiarrhythmics–use
atrial fibrillaiton
atrial flutter
ventricular tachycardia (amiodarone, sotalol)
what is the indication for class III antiarrhythmics?
when all other antiarrhythmics fail
sotalol toxicity
(class III antiarrhythmic)
torsades de pointes
excessive beta blockade
ibutilide–toxicity
(class III antiarrhythmic)
torsades de pointes
amiodarone–toxicity
(class III antiarrhythmic)
pulmonary fibrosis
hepatotoxicity
hypothyroidism/hyperthyroidism (amiodarone is 40% iodine by weight)
acts as hapten–corneal deposits, blue/gray skin deposits causing photodermatitis
neurologic effects
constipation
cardiovascular effects–bradycardia, heart block, HF
what should you always check when using amiodarone?
pulmonary function tests
liver function tests
thyroid function tests
amiodarone has effects of which classes and why?
I, II, III, IV
b/c lipophilic–alters lipid membrane
what are class IV antiarrhythmics and name 2?
calcium channel blockers
verapail
diltiazem
class IV antiarrhythmic–mechanism
dec conduction velocity
inc ERP
inc PR interval

class IV antiarrhythmic–use
prevention of nodal arrhythmias (eg. SVT)
rate control in atrial fibrillation
class IV antiarrhythmic–toxicity
flushing
constipation
edema
cardiovascular effects–HF, AV block, sinus node depression
name 2 antiarrhythmics other than those in classes
adenosine
Mg2+
what is the antiarrhythmic mechanism of adenosine?
inc K+ out of cells –> hyperpolarizes the cell and dec intracellular Ca
adenosine–use as a antiarrhythmic
diagnosing/terminating certain forms of SVT
how long does adenosine last?
~15 seconds
what are 2 things that block the effects of adenosine?
theophylline and caffeine–adenosine receptor antagonists
adenosine as a antiarrhythmic–toxicity
flushing, hypotension, chest pain, sense of impending doom, bronchospasm
when would you use Mg as an antiarrhythmic?
torsades de pointes
digoxin toxicity


