Cardiovascular Histology - Steve Flashcards
Arteries carry blood…
From heart to capillary beds
veins carry blood from… to…
Capillary beds to heart
What is the average diameter of a capillary?
~8um
Describe capillary structure

single layer of simple squamous epithelium (endothelium)
surrounded by basement membrane
What should you never see in lymph fluid?
Red blood cells
Compare the structure of blood capillaries vs. lymphatics
blood capillaries -uniform vessel diameter
lymphatic capillaries - variable lumen size, incomplete BM
most interchange between capillary lumen & extravascular space results from:
simple diffusion
rate depends on blood and colloid osmotic pressure
even capillaries w/o fenestrae (pores) very permeable
water
gases
salts
nutrients

How does capillary transport occur for soluble high molecular weight molecules?
numerous pinocytotic vesicles are present
50-70nm in diameter
transport soluble high MW molecules across endothelial wall

Describe what you see here

A cell passing endothelium by ameboid migration, called diapedesis
What is shown in red?

junctions between cells
interdigitations of the adjacent cell membranes
joined by tight junctions
What kind of membrane modifications do some organ capillary endothelium have? What organs have this?
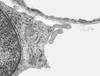
thin fenestrae (windows)
e.g. endocrine glands, renal glomerulus, intestinal villi
pores closed by diaphragm thinner than unit membrane
What type of cell is this? If is differentiates into smooth muscle, what function may it have on vessels?

Pericyte
May have a contractile function on the vessel
What are capillary support cells derived from (or similar to)? Where are they typically found?
mesenchymal-like cells
associated with, and surrounded by, capillary basement membrane
found intermittently
more common on post-capillary venules
Describe the role of pericytes in injury repair
in injury repair, can transform:
become vascular sm. muscle
also augment BM production
may function as fixed MØ’s
What is shown here?

application of adipose-derived adult stem cells
cells assume pericyte-like morphology
may play future role in wound healing and angiogenesis
What are the capillary types shown here?

Continuous capillary
fenestrated capillary
discontinuous capillary (sinusoid)
How do sinusoids differ from true capillaries?
larger than capillaries, with an irregular lumen diameter up to 30mm
sinusoidal endothelium
discontinuous in some locations
possess a discontinuous basement membrane
allows close association with parenchyma (functional cells)
Where are sinusoids typically found?
liver, spleen, bone marrow
continuous in some locations
hypophysis, adrenal glands
Some sinusoids possess phagocytic cells (mononuclear phagocytic system) What are two examples of these cells?
Macrophages (bone marrow and spleen), kupffer cells (liver)
What is shown in this image?

sinusoid of a lymph node
What are the layers indicated by the arrows?

tunica intima (TI): nearest the lumen
tunica media (TM): external to the intima
tunica adventitia (TA): outermost vessel coat aka tunica externa
What is the tunica media composed of on the arterial side? It is always the ______ layer on the arterial side.
Largely smooth muscle on the arterial side.
largest layer
What layer are we visualizing here? What are the labels associated with the arrows?

tunica Intima
endothelium
basement membrane
subendothelial CT
Inner elastic Lamina
Describe the morphology of the tunica intima
endothelium surrounds lumen
basement membrane underlies endothelium
subendothelial connective tissue
fibroblasts and CT fibers some of which run longitudinally
inner elastic lamina (IEL)
fenestrated layer composed of accumulated elastic fibers
outermost component of the tunica intima
visible when vessel is >60mm in size


































