Cardiology II Flashcards

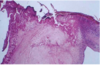
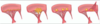
Fibrinous Pericarditis
- Shows thin strands of fibrinous exudate that extend from epicardial surface to pericardal sac

Fibrinous Pericarditis
Surface appears roughened from normal glistening appearance by strands of pink-tan fibrin

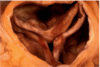
Fibrinous Pericarditis
Epicardial surface of heary shows shaggy fibrous exudate. “Bread & butter” pericarditis.
Fibrin often results in finding on PE of friction rub as strands of fibrin on epi/pericardium rub against each other
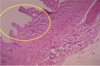
Microscopically, pericardial surface shows strands of pink fibrin extending outward w/ underlying inflammation.
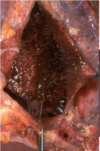
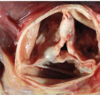
Hemorrhagic Pericarditis
Fibrous pericarditis + hemorrhage
W/o inflammation, blood in pericardial sac = hemopericardium

Hemorrhagic pericarditis
Surface of heart with hemorrhagic pericarditis has roughened, red appearance
Most likely to occur with metastatic tumor & TB

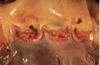
Suppurative/Purulent Pericarditis
Yellow exudate has pooled in lower pericardial sac. Usually implicates bacterial organism, and infection typically spreads from lungs.

Purulent Pericarditis

Xray of Dilated Cardiomyopathy (marked cardiomegaly)
Water bottle sign >1/2 chest width
Left heart edge appears far to the left

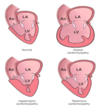
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Globoid shape because all chambers are dilated. Feels flabby & myocardium is poorly contractile.
Cardiomyopathy = poorly functioning myocardium and heart is large and dilated, but no specific histologic findings

Dilated cardiomyopathy
Large, dilated LV

Dilated Cardiomyopathy
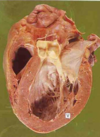
Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Cardiomyopathy
Microscopically, heart demonstrates hypertrophy of myocardial fibers (prominent dark nuclei) + interstitial fibrosis

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Marked LV hypertrophy w/ asymmetric bulging of large interventricular septum into LV
50% familial, though a variety of different genes may be responsible for the disease

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Narrowing of outflow tract before aortic valve - subaortic stenosis

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
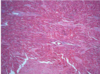
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
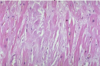
Myocardial disarray, not arranged parallel
Usually happens in fit, young adults and results fatally
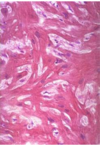
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Myocardial disarray (not arranged in parallel)

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy

Cardiac Amyloidosis
Cardiac Amyloidosis
Replacement of myocardium with amyloid (ECM, starch-like material)
>15 types of proteins that can result in amyloid deposition
Beta-pleated sheet configuration

Cardiac Amyloidosis
Congo red stain on myocardium
Amyloid stain orange-red, but with polarized light, the amyloid has apple-green birefringence

Cardiac Hemochromatosis
Excessive iron deposition can occur in heart, which leads to heart enlargement and failure similar to cardiomyopathy, making hemochromatosis a form of “restrictive” cardiomyopathy
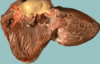
Acute Bacterial Endocarditis
Aortic valve has large, irregular reddish tan vegetation
Staph. aureus produces “acute” bacterial endocarditis, Strep. viridans produces “subacute”

Acute Bacterial endocarditis
More virulent bacteria cuasing acute bacterial endocarditis can lead to serious destruction
Irregular reddish tan vegetations can overlie valve cusps that are being destroyed. Portions of vegetation can break off and become septic emboli.
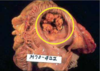
Acute bacterial endocarditis of AV valve