Cardiac Examination Flashcards
Cardiac Tings
cyanosis
Central cyanosis Peripheral cyanosis
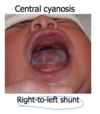
Central cyanosis
is blue discoloration of the mucous membranes and the fingers and toes. Central cyanosis occurs in the presence of right-to-left (venous to arterial) shunting of blood through an abnormal cardiac connection (ventricular or atrial septal defect).
Peripheral cyanosis
blue discoloration of the fingers and toes with sparing of the mucous membranes. Peripheral cyanosis occurs when there is a low cardiac output. -> low stroke volume, oseen in older people with low circulation.

Digital clubbing
painless Clubbing occurs in a variety of cardiac and pulmonary disorders that cause venous blood to mix with arterial blood. Congenital heart diseases characterized by right-to-left intracardiac shunts (Intracardiac shunting refers to the diversion of normal blood flow to alternate pathways within the heart as a result of a hole in structures that normally separate arterial from venous blood) are a common cause of digital clubbing.

NORMAL CARDIAC PRESSURES (conversion factor: 1 mm Hg = 1.3 cm H2O)

Ventricular systole

During systole,

Ventricular diastole is the time during which the ventricles relax and fill with blood.

During diastole

Know the pressures, S1 and S2, the isovolumerics, ejections diastolic fillings, depolarization (PQRST) waves.

What examine: jugular veins?

Central venous pressure (CVP)
what is its normal range?

How to measure central venous pressure
Identifying the different deflections of the venous pulse is best accomplished by comparing them to the timing of the 2nd heart sound or the radial artery pulse.

JVP is elevated when

Venous pulsations

“a” wave is

x descent

v wave

y descent



