Cardiac Anatomy Review-Cardiac Function Flashcards
What is a typical BP? what is a typical HR? CVP?
BP: 110/70
HR: 60-100
CVP: 5
WHat can be seen within the mediastinum on a radiograph?
hilar structures
position of trachea and
aortic arch
What things should you observe when looking at a heart radiograph?
cardiac size
pulmonary vessels
What should the width o fthe adult heart be?
less than half the greatest thoracic diameter, measured from inside the rib cage at its widest point near the level of the diaphragm
what wound a penetrating wound left of the sternum hit?
the right ventricle!! it is the most anterior part of the heart.
How can you tell based on anatomy whther you are looking at an AP or PA radiograph?
the heart and aortic arch are left of the midline
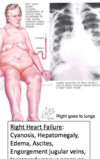
WHat is cardaic tamponade? what is the best measure when assessing for cardiac tamponade?
When blood or fluids fill the space between the pericardium and the heart muscle
venous pressure! It will continue to increase until it reaches arterial pressure and then they will both crash otgether

What are the layers of the pericardium from superficial to deep?
Fibrous pericardium
Parietal layer of the serous pericardium
Visceral layer of the serous pericardium
***note the pericardium is non-distenable, artists draw in a pericardial space so we can invision it but really it is just a layer of capillary thinning where the parietal and visceral layers rub against each other with a thin layer of viscous fluid in between
Where do you auscultate for the
- Aortic semilunar valve
- Pulmonary Semilunar valve
- Tricuspid Valve
- Mitral Valve
- Aortic semilunar valve: intercostal space 2, right of the sternum
- Pulmonary Semilunar valve: intercostal space 2, left of the sternum
- Tricuspid Valve: just lateral to the body of the sternum @ below rib 5
- Mitral Valve:apex of the heart at the intercostal space 5

WHat nerve runs along the lateral borders of the heart and what is the significance of that? Also what holds open the inferior vena cava?
Phrenic nerve!
So heart isues can irritate the phrenic nerve and lead to neck pain (bc the phrenic nerve runs up the neck)
Inferior vena cava is held open by the diaphragm

Label the arteries

- Right brachiocephalic
- Right subclavian
- Right common corotid
- Left common carotid
- Left subclavian
- Right coronary
During what part of the heart cycle do the coronary arteries perfuse?
coronary arteries perfuse heart during diastole.
- during systole the cornary arteries are blocked by the semilunar valves
- but during diastole, the blow backflows into the heart and the valves catch and the blood flows into the cornary arteries. This is how you get the sichortic notch on the whitters diagram bc the elastic recoil of the valves as they slap shut

Where are all of the places you acn take a pulse?
Superficial temporal artery
facial artery subclavian artery
radial artery
popliteal artery
dorsalis pedis artery
femoral artery
brachial artery
common carotid artery

Where would you inject the contrast in order to test the patency of the anterior interventricular artery?
Left coronary artery (LAD)
What is the farthest part of the heart to the anterior chest cavity?
Left atrium. it actually sits right in front of the esophagus
WHat does the left coronary artery branch into?
the left circumflex artery and the anterior interventricular artery (also known as the left anterior descending artery LAD)

What vein do the following arteries run with?
Anterior Interventricular Artery (LAD)
Right Marginal Branch of R Coronary
Posterior Interventricular Artery
- Anterior Interventricular Artery (LAD) travels with the Great Cardiac Vein
- Right Marginal Branch of the R coronary travels with the Small Cardiac Vein
- Posterior Interventricular Artery travels with the Middle Cardiac Vein

Describe the flow of blood starting in the body traveling back to the heart
Body
Inferior/Superior Vena Cava
Right Right Atrium
Tricuspid Valve
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Pulmonary artery
Lungs
Pulmonary vein
Left Atrium
Mitral Valve
Left Ventricle
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Aorta
Body
Describe where the SA node is
Describe where the AV node is
SA: Where the superior vena cava and the right atrium meet
AV: In the right atrium, part of th membranous septum

Where is the fossa ovalis?
in the right atrium. it connects the right and left atria.
10% of people have a probe patent atrium. usually doesn’t cause any problems, but coul dlead to a paradoxica embolism. aka a DVT found in an artery in the brain.

WHen does the tricuspid valve close?
when the right ventircular pressure increases. (to be equal to the right atria)

What is the function of the papillary muscles? what would happen if they were damaged due to an MI?
they maintain the competency of the tricuspid valve.
if they were damaged the tricuspid valve would have a foppy leaflet and not be compenetent. this would lead to hearing a murmur. you would hear the valve shut and then hear the bloo dflow back through the valve in the reverse direction

What is the yellow, what is the blue?
yellow is the mirtral valve. this is the valve beteween the left atrium and left ventricle.
blue is the papillary muscles that help maintain the valve