Carboxylic Acids and Derivitives Flashcards
(24 cards)
Inductive Effect
Creation of a strong dipole in a structure with different electronegative parts
How would the acidity of the structure differ and why?

The 2-bromoacetic acid would be more acidic due to the inductive effect of the bromine when compared to acetic acid.
Which will be a stronger acid?

Propanoic acid will be stronger because the methyl group on the 2-methylpropanoic acid donates electrons so in its base form it contributes to a more negative charge making it a less stable conjugate base

Place the following in order of increasint BP
hexane
hexanoic acid
heptanoic acid
hexanal
hexanol
hexane
hexanal
hexanol
hexanoic acid
heptanoic acid
Sapnification
xx
What would happen if you treated carboxylic acid with LiAlH4 and hydronium?
It would be reduced to a primary alcohol

How would you reduce a carboxylic acid to an aldehyde?
Treat it with DIBAL-H at low temps
Decarboxylation
CO2 is a product
Nucelophilic substitution reactions with carboxylic acids
The hydroxyl group can serve as a very good leaving group if turned to water so nucelophilic substitutions are really good for carboxy-acids. The OH essentially gets replaced with whatever.
eg
FIscher esterification
Hell Volhard Zelinsky Halogenation
What rxn:

DIBAL
True or false: The product of a Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction followed by hydrolysis is bound to be more acidic than the starting substrate
This statement is true. The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction followed by hydrolysis results in an α-brominated carboxylic acid. The inductive effect of the bromine on the α-carbon is guaranteed to make the resulting carboxylic acid more acidic than the parent chain that was reacted with a halogen and a catalytic amount of trihalogenated phosphorus.
What are the carboxylic acid dervitives?
Esters, Amides, and Acid Anhydrides
How would you name the following:

N-Methyl-Propanamide
What do you call a cyclic amide?
Lactams

True or False: amides tend to have weaker intermolecular interactions than alcohols and carboxylic acids (and therefore lower BPs)
True

Name:

Ethyl hexanoate
How would you name a ringed ester?
Lactone

True or False: Esters cannot hydrogen bond
True, this makes them rather volatile
True or False: Amids and esters dont tend to engage in acid base chemistry
true
If you condensed two acetic acid molecules, what would you get?
Acid anhydride
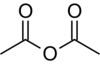
Name:

Butanoic ethanoic anhydride
Acid anhydrides are named for their alkyl chains in alphabetical order
Place the following in order of least to most reactive:
acid anhydride
caroxylate
carbocylic acid
acyl chloride
ester
acid anhydride
caroxylate
carbocylic acid
ester
acid anhydride
acyl chloride
What is the product?

This is the Hell-Vollhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction product prior to hydrolysis: an α-brominated acyl halide.



