Building Interactive JavaScript Websites Flashcards
(30 cards)
HTML script element src attribute
The src attribute of a element is used to point to the location of a script file.
The file referenced can be local (using a relative path) or hosted elsewhere (using an absolute path).

HTML script element defer attribute
The defer attribute of a tag is a boolean attribute used to indicate that the script can be loaded but not executed until after the HTML document is fully parsed. It will only work for externally linked scripts (with a src attribute), and will have no effect if it is applied to an inline script.
In the example code block, the tag will be loaded and parsed before the script is executed due to the defer attribute.
HTML script tag async attribute
Scripts are loaded synchronously as they appear in an HTML file, before the following HTML is loaded and parsed. The async attribute can be used to load the scripts asynchronously, such that they will load in the background without blocking the HTML parser from continuing.
In the example code block, the script will load asynchronously in the background, without blocking the HTML parser.

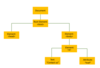
Nodes in DOM tree and HTML DOM
A node in the DOM tree is the intersection of two branches containing data. Nodes can represent HTML elements, text, attributes, etc. The root node is the top-most node of the tree. The illustration shows a representation of a DOM containing different types of nodes.
The DOM is an interface between scripting languages and a web page’s structure. The browser creates a Document Object Model or DOM for each webpage it renders. The DOM allows scripting languages to access and modify a web page. With the help of DOM, JavaScript has the ability to create dynamic HTML.
The DOM Parent-Child Relationship
The parent-child relationship observed in the DOM is reflected in the HTML nesting syntax.
Elements that are nested inside the opening and closing tag of another element are the children of that element in the DOM.
In the code block, the two
tags are children of the
, and the is the parent of both
tags.

The removeChild() Method
The .removeChild() method removes a specified child from a parent element. We can use this method by calling .removeChild() on the parent node whose child we want to remove, and passing in the child node as the argument.
In the example code block, we are removing iceCream from our groceryList element.

The element.parentNode Property
The .parentNode property of an element can be used to return a reference to its direct parent node. .parentNode can be used on any node.
In the code block above, we are calling on the parentNode of the #first-child element to get a reference to the #parent div element.

The document.createElement() Method

The element.InnerHTML Property

The document Object

The document.getElementById() Method

The .querySelector() Method

The element.onclick Property

The element.appendChild() Method

The element.style Property
The element.style property can be used to access or set the CSS style rules of an element. To do so, values are assigned to the attributes of element.style.
In the example code, blueElement contains the HTML element with the ID colorful-element. By setting the backgroundColor attribute of the style property to blue, the CSS property background-color becomes blue.
Also note that, if the CSS property contains a hyphen, such as font-family or background-color, Camel Case notation is used in Javascript for the attribute name, so background-color becomes backgroundColor.

.addEventListener()
The .addEventListener() method attaches an event handler to a specific event on an event target. The advantage of this is that you can add many events to the event target without overwriting existing events. Two arguments are passed to this method: an event name as a string, and the event handler function. Here is the syntax:
eventTarget.addEventListener(“event”, eventHandlerFunction);
.removeEventListener()
We can tell our code to listen for an event to fire using the .addEventListener() method. To tell the code to stop listening for that event to fire, we can use the .removeEventListener() method. This method takes the same two arguments that were passed to .addEventListener(), the event name as a string and the event handler function. See their similarities in syntax:

Event handler
When an event fires in JavaScript (such as a keystroke or mouse movement), an event handler runs in response. Each event handler is registered to an element, connecting the handler to both an element and a type of event (keystroke, eg.). A method called an event listener “listens” for an event to occur, specifies what should happen as a response, and calls the event handler.
Event object
Event handler functions are passed an argument called an event object, which holds information about the event that was fired.
Event objects store information about the event target, the event type, and associated listeners in properties and methods. For example, if we wanted to know which key was pressed, the event object would store that information.
Keyboard events
Keyboard events describe a user interaction with the keyboard. Each event describes a separate interaction with a key on the keyboard by the user, which are then stored with the .key property.
- keydown events are fired when the key is first pressed.
- keyup events are fired when the key is released.
- keypress events are fired when the user presses a key that produces a character value (aka is not a modifier key such as CapsLock).
javascript event
On a webpage, a trigger such as a user interaction or browser manipulation can cause a client-side JavaScript event to be created. Events can be used to manipulate the DOM by executing a JavaScript function.
Events can include anything from a click to hovering a mouse over an element to a webpage loading or being refreshed. Events are defined as a part of the JavaScript API built into the web browser.

JS Event Handlers
The goal of JavaScript is to make a page dynamic, which frequently means responding to certain events (for example, button clicks, user scrolls, etc). DOM elements can have functions hook onto events. The functions are called event handlers and the DOM element is known as an event target.
The example code block shows how to register a function as an event handler. The property name for event handlers starts with ‘on’ with the event appended afterwards. Examples: onload, onclick, onfocus, onscroll.

Mouse events
A mouse event fires when a user interacts with the mouse, either by clicking or moving the mouse device.
- click events are fired when the user presses and releases a mouse button on an element.
- mouseout events are fired when the mouse leaves an element.
- mouseover events are fired when the mouse enters an element’s content.
- mousedown events are fired when the user presses a mouse button.
- mouseup events are fired when the user releases the mouse button.
Handlebars.compile()
Handlebar.compile() can be used to produce a templating function. A template string with expressions must be passed into Handlebar.compile(). That function then takes an object as an argument, interpolates the object’s values into the template expressions, and returns a completed HTML string.









