BS - Pathology Flashcards
Rothmund-Thomson syndrome
growth retardation, thin eyebrows and lashes, juvenile cataracts, sunlight sensitivity, hypogonadism, and teeth
abnormalities. RTS is associated with an increased risk for cancer, such as cutaneous epitheliomas (basal, squamous), gastric adenocarcinoma, fibrosarcoma, and osteosarcoma
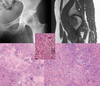
What is the structure
outlined by the black arrow in Figure 85b?

Birbeck granules (diagnostic of LCH)
LCH is also confirmed by CD1a
immunohistochemical staining.
cell membrane protein that conveys chemotherapeutic resistance to tumor cells
P-glycoproteins
protein produced from multidrug resistance gene 1 (MDR1)

scurvy
What percent of patients initially diagnosed with classic, high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremity have visible evidence of pulmonary metastasis on CT of the chest?
10-20%
Tumor syndromes + eponyms (7)
Ollier’s disease (enchondromatosis)
- Mafucci syndrome - enchondromatosis + soft tissue hemangiomas
MHE
Polyostotic Fibrous dysplaisa
* McCune Albright Syndrome: add cafe au lait spots in coast of Maine pattern, endocrine abnormalities (precocious puberty), renal phosphate wasing due to FGF-23 * Mazabraud's Syndrome: add intramuscular myxomas
NOF
- Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome: add cafe au lait, mental retardation, heart, eyes, gonads involved
EOG
- Hand-Schuller-Christian disease (HSC): chronic, disseminated form with bone and visceral lesions
- Letterer-Siwe disease (LSD): fatal form that occurs in young children
Frassica differential SURFACE LESION (5)
osteochondroma
MHE
parosteal osteosarcoma
periosteal osteosarcoma
periosteal chondroma (rare)
Frassica differential TIBIA (4)
fibrous dysplasia
osteofibrous dysplasia
adamantinoma
osteomyelitis
Frassica differential MULTIPLE LESIONS IN YOUNG PERSON
MHE
Ollier’s (enchondromatosis)
Fibrous dysplasia
EOG
Hemangioendothelioma of bone
Frassica differential ADULT BONE LESION
metastatic carcinoma
multiple myeloma
primary lymphoma of bone
chondrosarcoma
MFH (pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma)
Frassica differential HAND
enchondroma
GCT
ABC
giant cell reparative granuloma
Frassica differential EPIPHYSIS
GCT
clear cell chondrosarcoma
chondroblastoma
Frassica differential SYNOVIAL PROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS
synovial chondromatosis
gout
RA
PVNS
infection
Frassica differential SACRUM
chordoma
metastatic carcinoma
myeloma
lymphoma
Frassica differential BONE LESION YOUNG PERSON
osteosarcoma
Ewing’s sarcoma
osteomyelitis
EOG

fibrous dysplasia
most common distal met (distal to elbow/knee)
lung

GCT
curretage and BG or cement
Treatment?

CR + long leg cast

gout

pseudogout = pos birefringent
EOG treatment
observation

chordoma
-wide resection alone
60 yo, CD20 positive
Staging and treatment

bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are required for staging
cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone and vincristine