Brainstem part III: The Medulla Flashcards
What structures do we find in the medulla?
- Cranial nuclei for IX, X, XI and XII.
- The pyramids, and pyramidal decussation.
- Olivary nuclei.
- Aspects of other cranial nerves, the nucleus ambiguus, and nucleus solitarius.
- Reticular formation, ascending and descending tracts.
- Trigeminal
identify


identify

What do the olives (olivary nuclei) do?
- They send fibers to cerebellum via inferior cerebellar peduncle, and are involved with the cerebellum in the coordination of voluntary movement.
- connect the two cerebellar hemispheres, which makes sense since movements on both sides of the body need to be coordinated.
CN 11 has 2 parts, what are they?
nucleus solitarious receives what info?
cranial: part of nucleus ambiguous
spinal part: innervation of trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
taste information
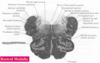
what part of the medulla is this?

caudal medulla
identify the parts of the caudal medulla


what cranial nerves come from behind the olives?
9 and 10
how many vestibuli nuceli are there?
what are they?
spinal tract and nucleus of trigeminal nerve, will extend to what spinal nerves?
2: medial and lateral
C2-C3
CN 9 will exit between what 2 structures?
In the caudal medulla the Lateral spinothalamic tract will be in the process of becoming what?
between olivary nucleus and pyramids.
spinal lemniscus
what do i look for when transitioning from the rostral medulla to caudal medulla?
nucleus cuneatus, nucleus gracilis + fasciculus cuneatus, fasciculus gracilis
what part of the medulla is this?
how do you know?

level of decussation of the pyramids
- you can see the fasciculus cuneatus and gracilis only, as well as the spinothalamic and spinocerebellar tracts and Spinal root of CN XI, going to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
What type of syndrome do we have in the picture?
what are the another 2 names for this type of lesion?

Medial Medullary Lesion
Inferior Alternating Syndrome or also known as Dejerne Syndrome.
Why does Medial Medullary Syndrome happen?
What symptoms do we see?
Occlusion/damage to anterior spinal artery, or vertebral artery
Symptoms:
- Contralateral hemiparesis.
- Loss of proprioception, vibratory and discriminatory touch.
- Ipsilateral paralysis of tongue muscles.
what type of syndrome will we see here?
what is another name for this?
What symptoms can we see here?
Lateral Medullary Syndrome of Wallenberg
PICA Syndrome
Symptoms include:
- Dysphagia
- Dysarthria
- Analgesia and thermoanesthesia on ipsilateral face
- Vertigo, nausea, vomiting, nystagmus
- Ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome
- Gait and limb ataxia
- Contralateral loss of pain and temperature sense
- dysphonia (hoarseness of voice) (damage to nucelus ambiguus)
Identify the blood supply to the different areas of the Medulla


identify the structures of the posterior medulla


what will you never see in lateral medullary syndrome?
tongue issues
dorsal column issues


