Brainstem Flashcards
(50 cards)
________________are the most posterior part of the diencephalon
Mammillary bodies
What are the three motor columns of the brainstem? Which nuclei are found in each column?
Somatic motor (general somatic efferent)
- Oculomotor nucleus
- Trochlear nucleus
- Abducens nucleus
- Hypoglossal nucleus
Branchial motor (special visceral efferent)- More lateral than somatomotor
- Trigeminal motor nucleus
- Facial motor nucleus
- Nucleus ambiguous
- Big motor nucleus
- Clusters of motor neurons going to the same target
- Can be divided into 10 different motor nucleu
Parasympathetic (general visceral efferent)- Near the midline but more dorsal
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- Superior and inferior salivatory nuclei
- Dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- Blood pressure and heart rate happen here, like in the Nucleus of solitary tract
What are the three sensory columns of the brainstem?
Visceral sensory (special visceral afferent)
•Nucleus of tractus solitarius (a.k.a Nucleus of solitary tract)
- Runs the full length of the medulla and is adjacent to dorsal vagus motor nucleus
General somatic sensory (general somatic afferent)
•Trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus
- Part of it is mesencephalic and some goes into the pons
- Trigeminal main sensory nucleus
- Trigeminal spinal nucleus
Special somatic sensory (special somatic afferent)
- Vestibular nuclei- Forms centered around pontomedullary junction and goes up to pons and low into medulla
- Superior
- Lateral
- Dorsal cochlear
- Inferior
- Medial
What are the three main components of brainstem?
Medulla Oblongata
Midbrain
Pons
Brainstem in sagittal section
Label


Brainstem with 4th ventricle exposed by severing cerebellar peduncles and cutting choroid roof away at the margins of the rhomboid fossa
Label


The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that stretch from the upper part of the _________ to the lower part of the __________.
midbrain; medulla oblongata
____________ nuclei are found predominantly in more rostral and median portions of the brainstem RF.
___________nuclei are generally located more caudally in medial and lateral parts of the brainstem RF
Modulatory; Premotor
What are the columns of the reticular formation?
Median (paramedian)
Medial (Central)
Lateral
What are the general functions of the reticular formations of the brainstem?
Activation and Integration
The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the ___________ in the ascending reticular activating system and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the __________ of the descending reticular formation.
cortex; reticulospinal tracts
____________ nuclei are getting input of sensory commands and their output is going to __________nuclei.
Premotor; motor
*Part of reticular formation is organizing motor actions like inputting signal and outputting to motor nuclei.
Cranial nerve nuclei locations
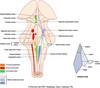
What nuclei are found in the median (paramedian) column of reticular formation?
Raphe nuclei
The Raphe Nuclei of the median reticular formation, project extensively to _____________.
Spinal cord, brainstem and cortical regions.
What neurotransmitter do raphe nuclei secrete? What is there primary function?
Serotonin
Participate in modulation of different functional systems, including motor, somatosensory, pain and limbic circuits.
NOTE: The serotonergic raphe neurons are part of the overall brainstem arousal system that includes cholinergic and dopaminergic reticular neurons that together have strong influence on attention, activity patterns and controlling periods of sleep and wakefulness (and also pain modulation)
Serotonergic neurons are located in a few different location serve different functions in those areas. Where are the different locations and where do they project?
- Serotonergic neurons in the rostral raphe complex of mesencephalon and rostral pons (ascending)
- Project mainly to forebrain targets.
- Serotonergic neurons in the caudal raphe complex of the caudal pons and medulla (descending)
- Project to the brainstem and spinal cord
Serotonergic neurons in nucleus raphe magnus are strongly involved in __________ and __________ through direct projections to the spinal cord dorsal horn.
Analgesia; pain modulation
NOTE: The Nucleus raphe magnus is apart of the raphe caudal complex
Where do serotonergic neurons of the nucleus raphe magnus project to?
Spinal cord dorsal horn
_____________ (lower/upper) raphe nuclei are involved in pain modulation and _________ (lower/upper) raphe nuclei are involved in arousal and sleep.
Lower; upper
What are some major medial (central) reticular nuclei?
•Cuneiform & subcuneiform (mesencephalic) nuclei
- Vertical gaze
•Oral pontine reticular nucleus
- Horizontal gaze
•Caudal pontine reticular nucleus
- Horizontal gaze
•Gigantocellular nucleus of medulla
- Horizontal gaze (rostral part)
- Horizontal head movement
The medial reticular column includes numerous nuclei serving premotor functions in concert with both somatomotor and branchiomotor nuclei.
Together they form “centers” for ____________
Chewing, facial movements, swallowing etc.
What type of neurotransmitters secreted by lateral column nuclei?
Catecholamine
What are some major lateral column reticular nuclei?
•Pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus
•Medial & lateral parabrachial nuclei (visceral sensory relay nuclei between Solitary tract nucleus & thalamus)
•Central pontine nucleus
•Central nucleus of medulla














