blood supply to the central nervous system Flashcards
outline needs of blood supply to the brain.
brain = 2% body weight
- 10-20% cardiac output
- 20% O2 consumption
- 66% liver glucose.
List sources of blood supply to brain.
Internal carotid arteries.
Vertebral arteries.
Circle of Willis
Cerebral arteries.
Label arteries of brain (inferior view=

Name components of venous drainage of brain.
Cerebral veins
Venous sinuses (formed from dura mater)
Dura Mater
Internal jugular vein
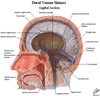
Label diagram showing dura mater sinuses
Define stroke.
rapidly developing focal disturbance of brain function of presumed vascular origin and of >24 hours duration
What proportion of strokes are infarctions.
85% (15% haemorrhage)
Define TIA.
rapidly developing focal disturbance of brain function of presumed vascular origin that resolves completely within 24 hours
Define infarction.
Degenerative changes which occur in tissue following occlusion of an artery.
Define cerebral ischaemia.
Lack of sufficient blood supply to nervous tissue resulting in permanent damage if blood flow is not restored quickly (relating both to O2 and lack of nutrients)
Name two cuases of occlusions.
Thrombosis
- formation of a blood clot (thrombus)
Embolism
-plugging of small vessel by material from larger vessel (e.g. thrombus from dislodged athersclerotic plaque)
Epidemiology of stroke.
Frequency, percetnage of survivors disabled, percentage survivors showing obvious neurological deficit.
3rd commonst cause of death
100,000 deaths UK/year
50%
70%
Name 5 main risk factors for stroke.
Age
Hypertension
Cardiac disease
Smoking
Diabetes Mellitus.
Understand areas of brain supplied by key arteries. Label diagram.

Cross sectional view of areas of brain perfused by key arteries. Label diagram.

Give 3 characteristics of stroke affecting anterior cerebral artery
Paralysis of contralateral leg > arm, face
Disturbance of intellect, executive function and judgement (abulia)
Loss of appropriate social behaviour
Give 4 characteristics of stroke affecting the middle cerebral arteries.
Contralateral hemiplegia: arm > leg
Contralateral hemisensory deficits
Hemianopia
Aphasia (L sided lesion) (speech)
Give characteristics of stroke affecting the posterior cerebral artery.
Visual deficits:
- homonymou hemianopia
- visual agnosia.
What is a risk factor for lacunar infarcts?
hypertension
What is a lacune
a small cavity
Where are Lacunes found?
In deep structures. A result of small vessel occlusion.
Deficit dependent on anatomical location.
List and outline 3 types of haemorrhagic stroke.
Extradural - trauma, immediate effects.
Subdural - trauma, delayed effects.
Subaracnoid - ruptured, aneurysms.
Intracerebral - spontaneous hypertensive.


