blood supply Flashcards
Anterior circulation
- INTERNAL CAROTID = 80% of blood supply
–> opthalamic
–> posterior cummunicating artery
–> anterior choroidal artery
–> anterior cerebral artery
–> middle cerebral artery
–> Ganlionic striate (lenticulostriate) arteries
ophthalmic artery
- main blood supply to RETINA
anterior choroidal artery
- supplies:
- -> OPTIC TRACT
- -> Choroid plexus
–> cerebral peduncles
- -> posterior limb of the INTERNAL CAPSULE
- -> globus pallidus
–> putamen and THALAMUS

Anterior cerebral artery
- Supplies MEDIAL ASPECT of the FRONTAL and PARIETAL LOBE and MEDIAL SENSORIMOTOR CORTEX
–> Pericallosal and callosomarginal
–> anterior choroidal
–> recurrent artery of Heubner
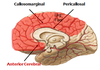
Pericallosal and callosomarginal
- Occlusion causes deficits, MOTOR AND SOMATOSENSORY, IN THE CONTRALATERAL LEG

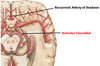
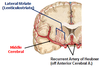
Recurrent artery of heubner
- supplies portions of the CAUDATE NUCLEUS, ANTERIOR PUTAMEN, GLOBUS PALLIDUS and INTERNAL CAPSULE
Middle cerebral artery
- Supplies virtually the entire LATERAL SURFACE of the cerebral hemispheres
–> superior division
–> inferior division
–> lateral striate (lenticulostriate) arteries
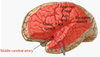
Superior division of middle cerebral artery
- Cortex above the LATERAL FISSUE
–> supplies lateral and frontal cortex including precentral and postcentral gyri

inferior division of middle cerebral artery
- Cortex below the lateral fissue
- Supplies lateral temporal lobe, parts of the PARIETAL LOBE

Lateral striate (lenticulostraite) arteries
- branches before MIDDLE CEREBRAL artery enters the lateral fissue
–> supplies BASAL GANGLIA and the internal capsule
–> prone to narrowing in patients with HYPERTENSION
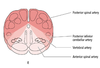
define watershed zones
- regions of the cortex between two cerebral vessels
- Infarcts in these areas can occur with severe drops in systemic blood pressure

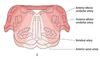
Posterior circulation
- VERTEBRAL = 20% of blood supply to cortex
–> posterior spinal artery
–> anterior spinal artery
–> posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
–> Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
–> superior cerebellar artery
–> pontine arteries
–> posterior cerebral artery

Posterior spinal artery
- off vertebral a
- Runs caudally on the dorsolateral aspect of the spinal cord
–> supplies dorsal region of the caudal medulla

Anterior spinal artery
- Off vertebral a
- Join its mate from the opposite side forming one single artery
- Runs along the ventral midline of the spinal cord
- PARAMEDIAN BRANCHES supply medial regions of the caudal medulla
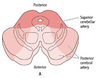
Posterior inferiron cerebellar artery (PICA)
- off vertebral a
- Long circumferential branch
- Supplies the inferior surface of the cerebellum, choroid plexus, lateral regions of the caudal medulla