Blood film Flashcards
Smudge cells

CLL
Hairy Cell

= Hairy cell leukaemia
Auer rods
= AML
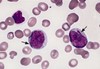
Red Cell Ghosts (black arrows)
Red Cell Ghosts - RBCs w/o Hb indicate intravascular lysis
Associations
-fulminant bacterial infections eg clostridium perfringens
Normocyte/Nucleated RBC

Not normal in peripheral blood
Association - severe haemolysis, hypoxaemia, myelofibrosis
Reticulocytes

Reticulocytes
Normally 1% of blood film
Increased when RBC turnover and creation is high - bleeding, haemolysis
Decreased when BM is suppressed - aplastic anaemia, systemic chemo
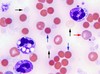
Teardrop/Dacrocyte
Associations - signify extramedullary haematopoiesis
- *- primary myelofibrosis**
- thalassaemia
Dohle Bodies

Associations
- infection
- inflammation
Hypersegmented neutrophil (>5 lobes)

Association
- Megaloblastic anaemia (B12, Folate)
- Rarely, iron deficiency anaemia
Rouleaux Formation

Associations:
- Infection
- *- Multiple myeloma**
- Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia
- Inflammatory and connective tissue disorders
- Malignancy
- *- DM** (a causative factor for microvascular occlusion in diabetic retinopathy)
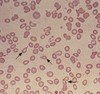
Basophilic Stippling

Associations
- Toxic injury to BM, such as lead or heavy metal poisoning.
- Severe anemia
- Thalassaemia
- Alcohol abuse
Polychromasia - premature release of RBCs

Associations
- anaemia, various causes
Spherocytes

Associations
- Warm and cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Acute and delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Hypophosphatemia
- Bartonellosis
- Snake bite
- Hyposplenism
- Severe burns
Blister Cells - precursor of bite cells (aka basket cells, half-ghost cells)
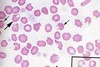
Associations:
- G6PD deficiency
- Unstable hemoglobins
Stomatocytes

Association:
- Artifact (due to slow drying in humid environment)
- Liver disease
- Alcoholism
- Rh-null disease
- Obstructive lung disease






