Blood Cell Identification Flashcards
1
Q

A
Neutrophil
2
Q

A
Neutrophil
3
Q

A
Lymphocyte
4
Q

A
Basophil
5
Q

A
Eosinophil
6
Q

A
Neutrophil
7
Q

A
Lymphocyte
8
Q

A
Monocyte
9
Q

A
Eosinphil
10
Q

A
Basophil
11
Q

A
Lymphocyte
12
Q
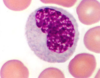
A
Monocyte
13
Q

A
Eosinophil
14
Q

A
Basophil
15
Q

A
Lymphocyte
16
Q

A
Monocyte
17
Q

A
Neutrophil
18
Q

A
Eosinophil
19
Q

A
Neutrophil
20
Q

A
Neutrophil
21
Q

A
Neutrophil
22
Q

A
Neutrophil
23
Q

A
Eosinophil
24
Q

A
Eosinophil
25

Eosinophil
26

Eosinophil
27

Monocyte
28

Monocyte
29

Basophil
30

Lymphocyte
31

Basophil
32

Eosinophil
33

Monocyte
34

Lymphocyte
35

Lymphocyte
36

Lymphocyte
37

Lymphocyte
38

Neutrophil
39

Lymphocyte
40

Monocyte
41

Eosinophil
42

Basophil
43

Basophil
44

Basophil
45

Lymphocyte
46

Neutrophil
47

Eosinophil
48

Basophil
49

Monocyte
50

Neutrophil
51

Lymphocyte
52

Eosinophil
53

Basophil
54

Monocyte
55

Monocyte
56

Basophil
57

Basophil
58

Eosinophil
59

Eosinophil
60

Neutrophil
61

Neutrophil
62

Monocyte
63

Monocyte
64

Monocyte
65
What cells are agranulocytes and granulocytes.
Agranulocytes: lymphocytes and monocytes
Granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
66
What antigens are on each blood type?
Type A - A antigens only
Type B - B antigens only
Type AB - A and B antigens (Universal recipients)
Type O - neither A nor B antigens (Universal donor)
67
What anti body's are on each blood type cell?
Type A - anti-B antibodies
Type B - anti-A antibodies
Type AB - neither anti-A nor anti-B antibodies
Type O - both anti-A and anti-B antibodies
68
What is sickle cell anemia?
Mutation of the hemoglobin gene causeing cells to look like crescent moons. They stick together causing impaired blood flow and oxygen delivery.
69
What is rouleaux?
RBCs form stacks due to unique disc shape cells. Forms when plasma concentration is too high. Can impair blood flow in small capillaries.
70
What is mononucleosis? (Mono)
Commonly caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and spread through saliva. Patients will have increased lymphocytes and 10% of them look like monocytes.
71
An immature erythrocyte that indicates a good response to blood loss
Reticulocyte
72
Giant marrow step cell that produces platelets
Megakaryocyte
73
Increase during allergic reactions
Eosinophil
74
Aid in the clotting cascade
Thrombocytes
75
Carry oxygen to cells
Erythrocyte
76
Stimulated by a hormone produced by kidneys
Erythrocyte
77
Responsible for adaptive immunity
Lymphocytes
78
Immature cells are called band cells and can indicate a response to infection
Neutrophils
79
Matured in the thymus, under the direction of thymocins
Lymphocyte
80
Produced from megakaryoctyes in the red bone marrow
Basophils
81
First responders
Neutrophils
82
Considered macrophages when in the tissue
Monocyte


