Block 1_Shoulder Flashcards
(24 cards)
What does Apley’s Scratch Test evaluate? What would be a positive sign?
Assymetry of shoulder movements. An assymetry may indicate problems with the glenohumeral joint or SITS muscles.
Which muscle does Empty Can Test (Jobe) evaluate? What would be a positive sign?
Evaluates integrity of supraspinatous muscle. Looking for assymetry in resistance (weakness) or pain.
Which muscle does Lift Off Test evaluate? What would be a positive sign?
Evaluates integrity of subscapularis muscle. Inability to lift hand off small of back, assymetry in strength, weakness, or pain may indicate pathology in subscapularis.
What does Shoulder Compression Test evaluate? What would be a positive sign?
Evaluates for tears in the glenoid labrum or other pathologies in the labrum. Looking for any clicking or poping or pain.
What does Yerguson’s Test evaluate? What would be a positive sign?
Evaluates for biceps tendon inflammation (specifically the long head of the biceps). Looking for pain.
What does Neer’s Sign evaluate? What would be a positive sign?
Evaluates for subacromial impingement or biceps tendonitis. Looking for pain.

What does Apprehension Test evaluate? What would a positive test be?
Guarding, apprehension, pain, or sensation of instability indicates anterior instability in glenohumeral joint. May be at risk for shoudler subluxation (partial dislocation) in anterior direction.
What does Sulcus Sign evaluate?
Looking for inferior instability. Tests for laxity allowing humerus to sublux out of glenohumeral joint then a sulcus (dimple just lateral to acromion process) would be produced.
What does Hawkin’s Sign evaluate? What would a positive sign be?
Pain would be a positive test. Evaluates for subacromial impingement. If there’s pain, then there could be inflammation in any of the structures of the subacromial space. More commonly it is inflammation of supraspinatous tendon. Reinforces Neer’s sign results or confirms a rotator cuff tear.
Which muscle does External Rotation Test evaluate? What would be a positive test?
Evaluates integrity of infraspinatous (90%) and teres minor (10%) muscles. Looking for pain or weakness.
How do you perform Apley’s Scratch Test?
Reach behind head as far down back as possible to “scratch” between scapulae. Measure level of thumbs.

How do you perform the Empty Can Test (Jobe’s)?
Patient flexes arms to 90 degrees. Abduct slightly to 45 degrees. Internally rotate humerus. Evaluator presses down on hands while patient resists.

How do you perform the Lift-Off Test?
Patient internally rotates arm and places hand on small of back. Then ask patient to lift hand off back. Evaluator may also resist this movement.

How do you perform the Shoulder Compression Test?
Patient flexes elbow to 90 degrees and abducts shoulder to 90 degrees. Evaluator then stabilizes shoulder and induces external and internal rotation while providing a force (medialy) through the shaft of the humerus so that the humerus is compressing the labrum.

How do you perform Yerguson’s Test?
Patient is seated. Locate the tendon of long head of biceps brachii, have patient flex elbow to 90 degrees with hand in pronation. Evaluator puts compressive force over intertubercular groove on the tendon. Patient then attempts to supinate hand and flex elbow against resistance.

How do you perform Neer’s Sign?
Patient seated. Evaluator depress scapula (stabilize scapula and clavicle) with one hand while passively moving the arm into flexion (at glenohumeral joint) with the other.

How do you perform the Apprehension Test?
Patient is seated. Evaluator flexes the elbow and abducts the arm. Then the evaluator applies extension and external rotation while applying anterior pressure on the scapula and proximal humerus.
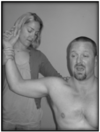
How do you perform Sulcus Sign?
Patient is seated. Evaluator stabilizes the scapula and clavicle and grabs onto the shaft of the humerus. Apply inferior traction while keeping shoulder stable.

How do you perform Hawkin’s Sign?
Patient is seated. Evaluator abducts arm to 90 degrees with elbow flexed at 90 degrees. Bring arm into flexion at 45 degrees. Stabilize under the elbow. Internally rotate humerus while maintaining superior pressure on inferior part of elbow.
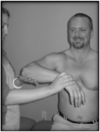
How do you perform External Rotation Test?
Patient flexes elbow joint to 90 degrees and internally rotates arm 45 degrees. Patient externally rotates against resistance.
What is the order of a shoulder exam?
- General observatory exam
- Lesions, rashes, etc. of shoulder
- Palpation (looking for TART) - BILATERAL!
- Jugular notch
- Manubrium
- Sternal angle
- Sternoclavicular joint
- Clavicle
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Corocoid process
- Pectoralis muscles
- Corocobrachialis
- Short head of biceps
- Deltoid
- Intertubercular sulcus
- Spine of scapula
- Trapezius
- Supraspinatous (tender point)
- Levator scapula tender point (superior border of scapula)
- Rhomboids
- Latissmus Dorsi
- Teres Muscles
- Axillary lymphadonopathy
- Proximal brachial pulse (2/4, regular rate and rhythm)
- Sensation to light touch
- Supraclavicular
- Superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm
- Intercostal brachial/medial cutaneous
- ROM (active, passive, strength testing)
- flexion
- extension
- abduction (feel scapulae)
- adduction
- external rotation
- internal rotation
What things should be palpated as part of a shoulder exam?
- Jugular notch
- Manubrium
- Sternal angle
- Sternoclavicular joint
- Clavicle
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Corocoid process
- Pectoralis muscles
- Corocobrachialis
- Short head of biceps
- Deltoid
- Intertubercular sulcus
- Spine of scapula
- Trapezius
- Supraspinatous (tender point)
- Levator scapula tender point (superior border of scapula)
- Rhomboids
- Latissmus Dorsi
- Teres Muscles
- Axillary lymphadonopathy
- Proximal brachial pulse (2/4, regular rate and rhythm)
What are the peripheral nerves of the shoulder?
- Supraclavicular
- Superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm
- Intercostal brachial/medial cutaneous
What are the motions of the shoulder?
- flexion
- extension
- abduction (feel scapulae)
- adduction
- external rotation
- internal rotation


