Block 1_General Flashcards
(24 cards)
TART stands for:
- Texture abnormalities
- Asymmetry of bony landmarks
- Restriction of motion
- enderness or soreness to examiner pressure
What things should you look for in a general observation?
- Wash hands
- Exam of axial skeleton and trunk
- Anterior
- Shoulders and clavicles
- Carriage of arms
- Hands
- Lateral
- Curvature of spine (accentuated)
- Cervical (Lordosis)
- Thoracic (Kyphosis)
- Lumbar (Lordosis)
- Plumb line (carriage of head)
- Curvature of spine (accentuated)
- Posterior
- Carriage of head
- Shoulder heights (scapula)
- Spine displacement (right or left)
- Scapula (distance from spine)
- Anterior
C5 is responsible for movement at this joint (myotome):
Shoulder abduction.
Myotome: C6 is responsible for which action?
Elbow flexion or wrist extension.
Myotome: C7 is responsible for which action?
Elbow extension or wrist flexion.
Myotome: C8 is responsible for which action?
Finger flexion or hand grip.
Myotome: T1 is responsible for which action?
Finger abudction/adduction
What are the dermatomes of the arm?

What are the peripheral nerves of the arm?

What is the DTR of C5 and how would you test it?
Biceps. Place thumb on biceps tendon and hit.
What is the DTR of C6 and how would you test it?
Brachioradialis. Hit just distal to the muscle belly just a little distal to where it starts to become tendonous.
What is the DTR of C7?
Triceps
Which cervical nerve root and thoracic nerve root do not have a DTR to test?
C8 and T1
How would you evaluate the C5 myotome?
Patient abducts shoulder bringing fists in towards chest. Evaluator pushes down on elbows.

How would you evaluate the C6 myotome?
With forearm in flexion, patient tries to flex forearm while evaluator tries to extend forearm.

How would you evaluate the C7 myotome?
With forearm in flexion, patient tries to extend forearm while evaluator tries to flex forearm.

How would you evaluate the C8 myotome?
With arm in supination and fingers in flexion, patient tries to flex fingers while evaluator tries to extend fingers.
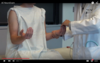
How would you evaluate the T1 myotome?
With fingers in abduction, patient triest to abduct fingers while evaluator tries to adduct fingers. Then, evaluator places fingers in-between patient’s fingers and asks patient to adduct fingers.

What type of bone is dense bone?
Cortical bone.
What type of bone is less dense?
Trabecular bone.
What does radioluscent mean?
Appears black. Things like air.
What does radiopaque mean?
Very white (e.g. metal).
If an x-ray is overexposed, what would we see?
Soft tissues look black (x-rays going through it and not bouncing back so we only see really dense things).
If an x-ray is underexposed, what would we see?
Soft tissues look really white. Can’t distinguish dense from less-dense.


