BIOMED - Pulmonary Stuff Flashcards
What is atelectasis, and what can PTs do about it?
Collapse of the lung, results from blocked airway or pneumothorax Deep breathing, posture, mobilization (generally), airway clearance (chest PT).
What is pneumonia and what can PTs do about it?
An acute inflammation / infex of the lung. We will hear diminished breath sounds but transmitted vocalization. See opacity on a chest x-ray Interventions: deep breathing, posture, airway clearance, minimize effects of inactivity (mobilization) - so… the SAME as atelectasis although they are different!
What are some causes of obstructive disorders?
Excessive secretions, thickened airway due to inflammation, loss of radial traction
How does an obstruction effect the body?
- Increased resistance to airflow 2. Greater pressure gradient - so, more work to breathe! 3. Effects EXPIRATION, more than inspiration. 4. FEV1 most affected (which predicts mortality) 5. Reduces ventilation/perfusion matching and air trapping occurs (dead space).
Common obstructive disorders?
- COPD (emphysema, chronic bronchitis) 2. Asthma 3. Cystic Fibrosis
What is a healthy FEV1/FVC ratio? What about in someone with obstructive disease?
80% In those with obstructive disease, the time it takes to expire is longer and in the end the amount available to expire is also less which yields a dramatically LESS ratio.
What is the resulting effect of restrictive disorders on the body?
Expansion of the lungs is restricted which limits ventilation
What are some examples of restrictive disorders?
Pleura Diseases: pneumothorax, hemothorax, pleural effusion Chest wall diseases: scoliosis, kyphosis, ankylosis gets spondylitis Neuromuscular Disorders: Weak muscles of inspiration (SCI)
What occurs to the FEV1 / FVC values in a person with restrictive lung disease?
Both values are diminished specifically even more with regard to time and the ratio becomes higher than 80%. Their expiration becomes very short because they don’t have enough air to breathe out.
Name the types of pulmonary imaging.
Chest X-ray VQ scan (inky) Bronchoscopy Spirometry (not imaging, but common dx)
What is the primary purpose of a chest x-ray and what are the primary things I would look at for interpretation?
- Bone/soft tissue: density, continuous, rib spacing 2. Heart/hilum: visibility, size 3. Diaphragm: costophrenic and cardiophrenic angles, location 4. Lungs: radiolucency/vascularity
Rank in order from most radiolucent to most radioopaque: Bone, Water, Tissue, Air
Air Water Tissue Bone
What are the differences between A and B and identify the pathological condition.

COPD
a) Increased chest wall size
b) Increased spacing between ribs -> hyperinflation
c) flattened diaphragm
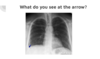
Identify the pathology in this image and say what could be the underlying cause of this pathology?

The Silhouette Sign: occurs when there is a loss of normal borders between thoracic structures.
This can be caused when there is a radiopaque mss that is formed near the heart or aorta.
Which muscles elevate and stabilize the upper ribs during inspiration?
Scalenes and SCM