BIOMED - Histology Flashcards
What are the 2 physiologic divisions of the respiratory tracts and what are there functions?
Conducting: transporting air to where it can undergo gas exchange. Respiratory: gas exchange!
What cell type makes up respiratory epithelium?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium w/ goblet cells
What are the main functions of the respiratory epithelium and the lamina propria?
Warm and humidify air Aid in immune response Trap particles in mucus and cilia to propel them out
What are the 4 layers of the trachea and what is generally found in each?
Starting from inner to outer: mucosa (epithelium and lamina propria) Submucosa (glands) Trachealis muscle / cartilage layer Adventitia (connective tissue)
Is the anterior or posterior region of the trachea more cartilaginous? And which is more muscular?
Anterior 2/3 is cartilage. Posterior 1/3 is trachealis muscle.
What type of cartilage will you find in the trachea?
Hyaline
The epithelial cells of the bronchus are __________ transitioning to _________.
Respiratory epithelium (as before, pseudostratified) Transitioning to simple columnar.
Smooth muscle is located in between what layers in the bronchus?
Just beyond the epithelial layer and superficial to the submucosa
How is the cartilage organized differently in the bronchus than it is in the trachea?
Cartilage is arranged in discs in the bronchus unlike in the trachea where it is a ring.
What part of the respiratory tract are Clara cells located and what is their function?
Lower respiratory tract, Bronchioles 1. Secretes a substance (surfactant) that decreases surface tension to prevent collapse of the airway (basically makes the lumen less sticky so it doesn’t stay stuck to itself and prevent an open airway). 2. Secretes substances which combat irritants. 3. Stem cells.
What are the 3 primary cell types of the alveoli? What are their functions and what do they look like?
Type I: minimum barrier to gas exchange and so they are squamous or flat in appearance. Type II: They produce and secrete surfactant, so they are cuboidal and between the junctions of 2 alveoli Dust Cells / alveolar macrophages: scavenge for particles that don’t belong in the alveoli - these are usually hanging out in the lumen.
What type of tissue is found in the lamina propria?
Lymph
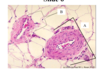
What is A, B, C?
What is this layer called?

A: Goblet Cells, which secrete mucus
B: Ciliated pseudostratified epithelial cells
C: basal stem cells
Respiratory Epithelium
What is A and what is it’s purpose?
What is D?
What is C and what is found here?
What layer is B and what can be found here?
What is E?
Where is this section from and how do we know?

Hyaline cartilage (which helps keep the airway open)
Respiratory epithelium
Lamina propia: lymph, blood vessels
Submucosa: contains ACH receptors (effect cilial mvmt and frequency), immunologic fx of serous/mucus glands
Adventitia
This is from the trachea because the hyaline cartilage is more ring-like than disc-like.
What type of tissue is *?
What tissue is at the arrow?
What part of the airway am I in and how do you know?

hyaline cartilage
smooth muscle
bronchi (most likely secondary), bc the cartilage is in discs, not a ring.
What layer is the arrow?
What layer is the pointer?
What is the *?
What is the tissue marked “a”?
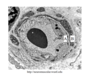
What structure is in the green circle?
What type of RE is present here?
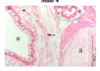
Smooth muscle
lamina propia
lumen
discs of cartilage
glands!
columnar epithelium