Biochemistry Unit Flashcards
(70 cards)
What are monomers?
units that combine to form polymers(macromolecules)
What are the monomers of proteins?
amino acids
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
nucleotides
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, fructose)
What are the monomers of lipids?
glycerol and fatty acids
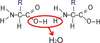
What process occurs to build a polymer(macromolecule)?
dehydration synthesis (water is releases during the process)
What process occurs to break apart a polymer?
hydrolysis (water is needed for this to occur)
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
What is the property of water demonstrated when water stickd to a different substance?
adhesion
What is the property of water demonstrated when water froms droplets because it sticks to itself?
cohesion
What property of water allows water to travel up the stem of a plant against gravity?
capillary action (adhesion and cohesion together allow this to occur)
What property allows water to be cohesive?
water is polar …called polarity…because oxygen portion has a negative charge and the hydrogen portion has a positive charge
What is polarity?
oxygen portion has a negative charge and the hydrogen portion has a positive charge
What kind of bond forms between 2 water molecules allowing cohesion to occur?
hydrogen bond…which is an attraction of opposite charges (positive hydrogen on one water molecule is being attrated to other water molecules negative oxygen)
What is the universal solvent and why?
Water…because it is polar and can dissolve many molecules
What are the three monosaccharides?
glucose, galactose, and fructose
What do animals store their polysaccharides as? Where do animals store thispolysaccharide?
animals store many many glucose molecules joined together to form a molecule called glycogen ….glycogen is then stored in the skeletal muscle and liver until it needs to be released into the blood stream
What are the two plant polysaccharides?
starch(what we consumers eat) and cellulose(component of paper and plant cell walls)
What are the functions of carbohydrates for living things?
energy and make up cell wall in plant cells
What is the function of nucleic acids for living things?
store, transmit hereditary information …….DNA has the codes to make proteins
What are the functions of lipids for living things?
insulation, waterproof barrier, makes up major part of the cell membrane, stored energy, steroids hormones
What are the functions of proteins for living things?
enzymes (like catalase), protein hormones(like insulin), storage, transport (like hemoglobin), structural (like collagen, elastin, keratin), defensive (like antibodies), channels in cell membrane (like sodium potassium pump or ATP synthase), contractile (like actin and myosin)
A protein that increases the rate of a chemical reaction
enzyme
catalyst
an enzyme that speeds up a chemical reaction