Bilder KMP 4 Flashcards
Diagnose?

Chronische Analfissur
(Länglicher belegter Ulkus + Sekundär: Hypertrophe Analpapille, narbige Ränder)
Diagnose?

Sekundäre Analfissur durch CED, Lues ecc.
-> HÄUFIG INDOLENT + ATYPISCHE STELLE

II.Prolaps bei Defäkation = spontan retrahierend
Diagnose?

IV.Grad Prolaps = fixiert, thrombosiert, irreponibel
- Grad = nur proktoskopisch + vergrößert
- Grad = Spontan retrahierend -> spontan reponiert
- Grad Prolaps bei Defäkation -> manuell reponierbar
- Grad = Fixierter Prolaps + nicht reponierbar
Diagnose?

Perianale Venenthrombose = akut-schmerzhaft (Analvene am Rand)
Diagnose?

Ältere perianale Venenthrombose
Diagnose?

Abszess/Fistel
Diagnose?

Condyloma acuminata = Feigwarze
Diagnose?

Condyloma acuminata

- Perianale Venenthrombose
- Analfissur
- Hämrrhoidalleiden
Diagnose?
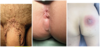
- Condylomata acuminata
- Analabzess
- Normaler Abszess
Diagnose?

Hämorrhoiden -> rote Zone markieren

->Stevens-Johnson-Syndrom (SJS) und die toxisch epidermale Nekrolyse (TEN) sind schwere Überempfindlichkeitsreaktionen der Haut. Meist sind Arzneimittel, v. a. Sulfonamide, Antiepileptika und Antibiotika, die Auslöser.










Lobärpneumonie linker Oberlappen
Zuordnen: Coekum, Mesenteriolum, Appendix!

- Appendix
- Mesenteriolum
- Coekum
Diagnose?

Aneurysma
Diagnose?

Atelektase

Intetrigo
Was zeigen die 3 Pfeile?

Dünner gestrichelter Pfeil: Hungerdarm
Dicker Pfeil: Lufteinschlüsse
Dicker gestrichelter Pfeil: Prästenotische Dilatation
Ileus ->Prästenotische aufgeweitete Dünndarmschlingen mit postsenotischem Hungerdarm.

Diagnose?

Peritonitis Grad IV