Bayesian Statistics Flashcards
What is a central factor to the likelihood approach to statistics?
Only the data is random, parameters are unknown but constant.
What does MLE stand for? How is it found?
Maximum likelihood estimate - found by maximising the likelihood function
What is the Bayesian approach to statistics?
Everything is unkown is a random variable and is associated with its own probability distribution.
Define the multiplication rule.

Define the partition theorem.

Define conditional independence.

Define Baye’s theorem for continuous random quantities.

What are the four steps in a general Bayesian analysis?
- Prior
- Data
- Posterior
- Inference
What is meant by the prior stage in Bayesian analysis?
Before seeing data X, specify uncertainty about θ, f(θ) - the prior distribution for θ
What is meant by the data stage in Bayesian analysis?
We observe {Xi=xi}, obtain the likelihood as x given θ - f(x|θ)
What is meant by the posterior stage in Bayesian analysis?
After seeing data {Xi = xi} update distribution for θ:
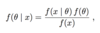
What is meant by the inference stage in Bayesian analysis?
Answer questions about θ.
What is the equation for the following?
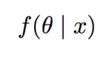
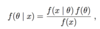
What is meant by the following eqaution?


Why do we have the following?

If f(x) is constant in the following.
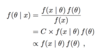
What are the two types of priors?
- Informative
- Non-informative
What is an informative prior?
f(θ) encodes specific information about θ
What is a non-informative prior?
f(θ) deliberately vague about θ
What is an improper prior?
One that doesn’t integrate to 1
Define conjugacy.

What does conjugacy imply about the prior and posterior?
Have the same functional form, same distributions
Define the core (kernel) of a distribution.

What is a lemma about the core of a distribution?

Prove the following lemma.


Define the Beta distribution.

What are four important properties of the Beta distribution?

What is the Beta-binomial theorem?

Prove the following theorem.


Define the Gamma distribution.

What are three important properites of the Gamma distribution?

What is the Gamma - Poisson model theorem?

Prove the following theorem.


Prove what the posterior mean is for the Beta-binomial model.

What are three important properites of the Gamma - Poisson model?