Basic Principles of Infectious Diseases L15 Flashcards
Infectious disease is caused by which pathogenic microorganisms? (3)
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Parasites
List the routes of transmission of infectious disease. (6)
- Contact
- Aerosol
- Faeco-oral
- Sexual
- Animal vector
- “Mechanical” (e.g. needle-stick, insect bite)
Define obligate intracellular parasites.
E.g.?
Obligate intracellular parasites cannot reproduce outside their host cell, meaning that the parasite’s reproduction is entirely reliant on intracellular resources. Can only live within living cells.
E.g. Viruses
What do viruses not have that they need from living cells? (3)
- Organelles
- Raw material for reproduction
- Enzymes
etc.
A virus basically consists of a nucleic acid packaged up in a ____1____, and in some cases wrapped up in an ____2____.
- Protein
- Envelope
Disease outcome depends on type of pathogen and ability of immune response to clear the infection. An ____1____ viral infection is characterized by rapid onset of disease, a relatively brief period of symptoms, and resolution within ____2____. It is usually accompanied by early production of infectious ____3____ and elimination of infection by the host immune system.
- Acute
- Days
- Virions
A chronic infection is a ____1____-lasting infection Chronic infection occurs when the host immune response is able to ____2____, but not eliminate, the infecting organism In chronic infection the infecting organism continues to ____3____ at a low level In latent infection the infecting organism is dormant and does not ____3____. Some infections may have both a chronic and latent phase.
- Long
- Control
- Replicate
What is the longest a chronic infection can last?
A lifetime.
Give example of bacterial chronic infections. (invading organism, disease caused) (2)
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis - tuberculosis
- Mycobacterium leprae - leprosy
Give example of parasitic chronic infections. (invading organism, disease caused) (2)
- Plasmodium falciparum - malaria
- Schistosoma – schistosomiasis
Give example of viral chronic infections. (3)
- HIV-1
- Hepatitis B virus
- Hepatitis C virus
Hep _1_ 90% cases = Acute infection 10% cases = Develop a chronic infection
Hep _2_ 20% cases = Acute infection 80% cases = Develop a chronic infection
- B
- C
____1____ live inside the macrophage and are able to resist the immune response. They replicate inside the endosomes.
- Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium tuberculosis form a ____1____ in the lung leading to tuberculosis. Mycobacterium leprae live in cooler regions (such as skin and nose) and also infects ____2____ cells leading to nerve degeneration in leprosy.
- Granuloma
- Schwann
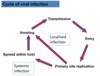

Read
Cycle of viral infection
Entry
- Virus attaches to cell by binding a cell surface receptor.
Penetration
- Either through receptor-mediated endocytosis or by fusion of viral envelope to membrane and subsequent release of rest of virus.
Uncoating
- Viral genome is unwrapped (protein coat is removed).
Biosynthesis
- Of new nucleic acid (genome) copies.
- To produce new viral proteins.
Assembly
- New viral proteins package up viral genome copies.
Release
- Via exocytosis or lysis of cell.
Viruses require the host cell ribosomes, enzymes, precursors etc. to generate the new proteins and genomes. This is why they must live inside cells.
Describe an asymptomatic/subclinical infection.
No adverse symptoms – virus cleared by immune response
or
Establishes persistent infection
Describe an acute infection
Illness lasts a few days/weeks – virus then cleared by immune response
or
Establishes persistent infection or death
Describe an chronic infection
Virus not cleared by immune response - continuous production of virus progeny
Describe latent infection
Viral genome is maintained in host cells for many years until re-activated (e.g. by stress). No progeny during latent period.
How the acute infection progresses is dependent on how well your immune response is able to control the infection.

Enzymes of virus genome replication and transcription
dsDNA and ssDNA can often be replicated by ______ ___1___ ______ and transcribed by ______ ___2___ ______.
- Host DNA polymerase
- Host RNA polymerase
Enzymes of virus genome replication and transcription
dsRNA and ssRNA require an ______ ______ 1 ______ ______ (RdRp) for replication and translation: must be encoded by ____2____.
- RNA dependent RNA polymerase
- Virus





