Basic concepts of Ornithology Flashcards
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars

Primaries
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars

Primary Coverts
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars

Marginal Coverts
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars

Secondary Coverts
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars

Scapulars
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars

Secondaries
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars
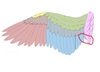
Tertials
What part of the wing is this?
Word Bank:
Primaries, Secondaries, Tertials, Primary Coverts, Secondary Coverts, Marginal Coverts, Alula, Scapulars
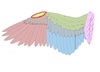
Alula
4 keys to field ID
Shape, Color, Behavior, Habitat
Bristles
Act like eyelashes, protecting, and to sense prey

Down Feather
Primarily serve as insulation

Filoplumes
Used for sensory, possibly in flight - wind direction, feather placement during flight

Retrices
Tail feathers

Aftershaft

Rachis

Vane

Powder Down
Powder downs, which occur in a variety of birds, including some parrots, are specialized feathers, usually found in well-defined patches, that produce a powdery substance used to clean and waterproof the other feathers.
Apteria
Spaces without feathers

Pterylae
Linear tracts of feathers

Brood Patch
Patch of featherless skin on breast during nesting, transfers heat to incubating eggs.

Carotenoid
Carotenoids produce bright reds, oranges, and yellows. Many of the foods that birds eat, such as berries, seeds, and insects are loaded with carotenoids, and birds must ingest these carotenoid-rich to color their feathers.
Melanin
Melanins produce mainly earth tones, such as black, brown, reddish brown, gray and olive colors. Birds can produce melanins from the basic amino acids that occur naturally in the body.
Structural Colors
Produced by the interaction of light and the microscopic structure of the surface of the feather, not by pigments. The microscopic structureof the feathers absorbs longer wavelengths and reflects the shorter wavelengths. This produces bright blues and greens as well as UV coloration. White feathers are an example of structural coloration where there are no underlying pigments and all visible wavelengths are reflected back.
Plumage
All of the bird’s feathers collectively






















