Basic Breast and Pelvic Exams Flashcards
Basic surface anatomy of female genitalia

Location of Bartholin’s glands
Note that these are not normally visible unless enlarged or inflammed

Preparation for female pelvic examination
- Explain purpose of exam and ask for permission
- Request that the patient empty her bladder
- Ensure that examination equipment is within reach: light source, vaginal speculum of appropriate size in warm water, materials for Pappanikalou smear, bacteriologic cultures, or other requried instruments, water soluble lubricant, cotton suaves, examining gloves, tissues
- Assistance of third party (nurse) usually indicated
- Be aware at all times that the patient may be apprehensive and do whatever necessary to make patient feel comfortable
Anatomy of cervix as viewed from inside the vagina

Why can you not use a gel lubricant for vaginal exams?
Because it will interfere with bacterial culture and proper Pap smear sampling, which are usually the indications for vaginal exam in the first place.
What should you do if the cervix does not come into view upon inserting the speculum?
Withdraw the speculum slightly and reposition it with a different slope.
This is a common occurence, as the anatomy of the cervical-vaginal junction often differs between patients.
Indications for taking a sample upon cervical exam
- Malodorous
- Colored discharge (clear discharge of varying thickness is normal, yellowish suggests mucopurulent cerivicitis)
What are the likely causes of there is mucopurulent discharge coming from the cervix?
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- HSV 1 or 2
What are the likely causes of there is mucopurulent discharge coming from the vaginal wall?
- Candida species
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Trichomonas vaginalis
How should one move the cervical broom in order to take a proper Pap smear sample?
- 360o clockwise rotation with the tip inserted into the cercal os such that the squamo-columnar epithelial junction is sampled, enabling observation of both the squamous vaginal epithelium and the columnar uterine epithelium
- When brushing the slide, both sides of the broom should be brushed to ensure a complete sample
What Pap smear sampling tool should be used in pregnant women?
A cotton-tipped applicator moistened with warm saline
Do NOT use a cervical broom or brush
Positioning for a uterine exam

Adnexal
Basically means para-uterine. Used to describe the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and connective tissue supporting the uterus.
“Full strength” pelvic floor muscles
Contraction of fingers that moves them upward and inward and lasts for at least 3 seconds
What is the advantage of having a male patient stand for a genital exam?
Varices and hernias are better visualized
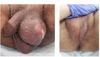
The depicted lesions are seen on a male patient’s routine genital exam. What are they?

Epidermoid cysts. Benign and common, no need for treatment or concern.
Where should the epididymis be palpable on scrotal exam?
Superiorly and posteriorly.
Should feel cord-like, but not have any lumps
One effective way to determine whether a femoral or inguinal lesion is a hernia is to . . .
. . . listen for bowel sounds with a stethoscope
What to do if you find a hernia on physical exam
Attempt to return it to the abdomen by applying mild pressure, but do not continue if the patient reports pain, nausea, or gag reflex
When is testicular self-examination best performed?
After a warm bath or shower
Breast surface anatomy

Systematic breast exam
There is evidence that the linear method is more effective than others, so this should be employed

Distended bladder
Note that the swelling is below the level of the umbilicus

Tinea cruris vs candidal intertrigo