Basal Ganglia Anatomy and Function Flashcards
Frontal slide through the cerebrum showing both sides of the brain
White grey= grey matter; dark grey= white matter

Where are the basal ganglia located?
deep within the cerebrum (or telencephalon), the front most part of the brain

What are the basal ganglia?
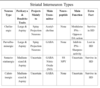
Caudate
Putamen
Globus pallidus (internal and external)
Why is the substantia nigra black?
because it contains nuclei that contain black melanin
Close up of the basal ganglia. Where is the caudate nucleus located?

medial and along the lateral ventricles
IC= internal capsule
CC= corpus callosum
The basal ganglia are primarily involved in what?
movement control (somatic basal ganglia mostly)
motivation, reward, and affect (limbic basal ganglia)
The basal ganglia can be divided into what two categories of structure?
the somatic basal ganglia (dorsal) and the limbic basal ganglia (ventral)
What is the limbic basal ganglia composed of?
the nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercles, and the ventral pallidum
Note that the somatic BG include the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus
Left side view of the basal ganglia.
Note that the internal capsule seperates the caudate nucleus from the putamen in space

The tail of the caudate wraps behind and then ventral underneath the putamen to end as what structure?
amygdaloid nucleus
Note how the putamen and caudate nucleus are collectively called what?

the striatum


This image is a brain with a stain showing which nuclei make dopamine. Notice how the substantia nigra is the most dominant dopamine making nuclei
You can also see that the putamen, and the head and tail of the caudate are all brown. Why?

Because the substantia nigra ha axons that travel into the head of the caudate, the putamen, and tail of caudate, and form dopaminergic terminals there (the globus pallidus does not receive many dopamine terminals, so its pale)
The _____ ______ is the midbrain continuation of the internal capsule
the cerebral peduncle
Note the labels individual dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Where are they located?

in an upper part of the substantia nigra, called the pars compacta (because they are arranged in a compact layer)
The region beow the pars compact is called what?
the pars reticulata (a reticulum is a net-like meshwork of fibers) - note that this area contains few dopaminergic neurons. Rather, its neurons commonly very much resemble those in the globus pallidus in their chemistry, shape and function.
Thus, while the pars compacta and the pars reticulata together make up the substantia nigra, only the pars compacta really contains melanin

What neuron types make up the striatum?

A (aspiny) neurons and SN (spiny) neurons
In the striatum, 5% are A neurons
Describe A neurons
An aspiny neuron has dendrites that do not possess stubby protrusions on them (the stubby protrusions are called spines). About 95% of neurons in the striatum are SN neurons
T or F. SN neurons are usually smaller than A neurons
T.
Closeup of a SN neuron. Again, A neurons are larger than SN neurons
Neurons that need to integrate info from diverse sources possess dendritic spines

One important point about spiny neurons is that they have what?

a long axon that leaves the striatum (by contrast, A neurons have axons that are short and dont leave the striatum)
Because of this, SN neurons in the striatum are called projection neurons, while the A neurons are called the local circuit neurons, or interneurons. Thus, it is spiny neurons that transmit decisions to other brain areas
All spiny neurons use what neurotransmitter?
GABA
What are the different types of projection (spiny) neurons based on?
-type of neuropeptide contained (neuropeptides are adjunct neurotransmitters that neurons often use, but they also can be neurochemical signatures for defining neuron subtypes)